
FAIR is a non-profit organization dedicated to providing well-documented answers to criticisms of the doctrine, practice, and history of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.
Jump to Subtopic:
Life and Character |
|
Youth |
|
Revelations and the Church |
|
Prophetic Statements |
|
Society |
|
Plural marriage (polygamy) |
|
Death |
There were many contributing factors which led to the martyrdom. Chief among these include:
The factors which led to the martyrdom of Joseph and Hyrum Smith are complex and multi-faceted. They included the following:
There were other factors that led to Joseph's martyrdom, including economic, social, and cultural tensions between Mormons and non-Mormons.
All of this was dry powder that was finally sparked by the publication and suppression of the Nauvoo Expositor. If one reads the Expositor, one can see all of the reasons listed above as grievances dissenters gave against Joseph Smith. Because of its highly incendiary and threatening language, the Nauvoo city council deemed the paper a public nuisance and voted to stop its publication out of fear that allowing its continued publication would lead to mobs and violence against the Saints. Acting under the direction of the city council and Joseph Smith, the Nauvoo city marshal destroyed the press that printed the Expositor.
This, naturally, led to a public outcry against Joseph Smith. Thomas Sharp, the virulent anti-Mormon editor of the Warsaw Signal, infamous proclaimed upon hearing about the destruction of the Expositor,
War and extermination is inevitable! Citizens ARISE, ONE and ALL!!!—Can you stand by, and suffer such INFERNAL DEVILS! to ROB men of their property and RIGHTS, without avenging them. We have no time for comment, every man will make his own. LET IT BE MADE WITH POWDER AND BALL!!!
At the behest of governor Thomas Ford, and after being discharged of charges of inciting a riot by a non-Mormon justice of the peace, Joseph went to the county seat in Carthage, where he again faced charges of inciting a riot and the destruction of private property. After paying bail of $500 dollars, there suddenly came the bogus charge of "treason," a non-bailable offense, by dissenter Augustine Spencer, and justice of the peace Robert Smith order Joseph and Hyrum kept in Carthage. To be frank, the charge of treason was probably little more than a legal pretext to keep Joseph in Carthage, and was likely part of Thomas Sharp's conspiracy to lynch Joseph.
Despite his pledge to protect Joseph, Ford, at the last minute, disbanded his militia troops, apparently out of a concern that if they accompanied him to Nauvoo they'd cause trouble, and told them to go home. But left behind in Carthage as Ford traveled to Nauvoo were the Carthage Greys, in whose ranks some of the most fanatical and bloodthirsty anti-Mormons, including members of Thomas Sharp's Warsaw militia and Sharp himself, were marshaled. Small wonder that Joseph was murdered by the Greys almost as soon as Ford left Carthage for Nauvoo.
It is claimed that prior to leaving for Carthage, that Joseph Smith removed his garments, and advised others to remove theirs, in order to avoid identification as polygamists. [1]
Of the four men who were in Carthage Jail at the time that Joseph and Hyrum Smith were killed, three of them had removed their garments prior to leaving Nauvoo. Willard Richards was the only one of the four who was wearing his garments at the time of the martyrdom.
The commonly believed reason for the removal of the garments was that they were removed in order to keep them from falling into the hands of their enemies. Heber C. Kimball reported in his journal that Joseph instructed those of the Quorum who were going to accompany him to Carthage to remove their temple garments prior to leaving.[2] Sarah G. Richards noted the following in a letter to Zina Huntington,
[T]he order came that in every habitation where any of the endowment clothes were found, [it] would [mean] death to the inmates—Olive Frost...came to tear to pieces the garments &c of...Doctor Levi....Miss [Rhoda] Richards separated the parts and placed them among the articles of linen.[3]
Oliver Huntington elaborated on this in his journal entry for 22 April 1897:
Thursday, April 22, 1897: My niece Zina Card and sister Lucy B. Young came on their return from Goshen and the other settlements in this county south of here and stayed all night with us.
They were out by appointment from the Presidency of the Church in the interests of the young womans Journal.
We had an excellent time while they were here talking over old times, the sayings of Joseph and Hyrum of Brigham and others.
Among other things both new and old was repeated the fact that the Prophet Joseph pulled off his garments just before starting to Carthage to be slain and he advised Hyrum and John Taylor to do the same, which they did; and Brother Taylor told Brother Willard Richards what they had done and advised him to take off his also, but Brother Richards said that he would not take his off, and did not; and he was not harmed.
Joseph said before taking his garments off, that he was going to be killed. . . "was going as a lamb to the slaughter" and he did not want his garments to be exposed to the sneers and jeers of his enemies.
These facts all came from President John Taylor's lips after he was President of the Church. Elder John Morgan had told them to me as stated to him by Brother Taylor. Sister Lucy B. Young said that Brother John Taylor told her in answer to direct questions, the same all except with regard to Willard Richards.[4]
It appears, therefore, that garments may indeed have been removed in order to prevent them from being mocked. Critics, however, assumed that the garments were removed because Joseph and the others were somehow afraid of wearing them in the presence of their enemies. John Taylor, who was one of the four present in the jail at the time of the Joseph and Hyrum's death, responded to this by clarifying that the garments were sometimes removed simply because of the hot Illinois weather.
Elder John Taylor confirmed the saying that Joseph and Hyrum and himself were without their robes in the jail at Carthage, while Doctor Richards had his on, but corrected the idea that some had, that they had taken them off through fear. W. W. Phelps said Joseph told him one day about that time, that he had laid aside his garment on account of the hot weather.[5]
The fact that Willard Richards was the only one who escaped the martyrdom unscathed appears to have led to the belief that he had been protected because he was the only one of the four wearing his garments at the time.
[Elder Kimball] Spoke of Elder Richards being protected at Carthage Jail—having on the robe, while Joseph & Hyrum, and Elder Taylor were shot to pieces.[6]
This idea that the garments would have physically protected Joseph and Hyrum was further elaborated on by Hubert Howe Bancroft in his History of Utah. Bancroft notes the following regarding the temple garment,
This garment protects from disease, and even death, for the bullet of an enemy will not penetrate it. The Prophet Joseph carelessly left off this garment on the day of his death, and had he not done so, he would have escaped unharmed.[7]
Modern-day Church leaders have since clarified that the temple garment serves as "a protection against temptation and evil" and instead of it being some type of 'lucky talisman' the "promise of protection [associated with it] is conditioned upon worthiness and faithfulness." (First Presidency Letter, 10 October 1988; see Ensign, August 1997, 19-).
The wearing of garments was used by those hostile to the Church as a means of identifying Mormons. In the autobiography of B.H. Roberts, Elder Roberts relates the story of how an "Elder Robinson" removed his garments while in hostile territory in order to avoid being identified as a Mormon.
But unfortunately if Elder Robinson should fall into the hands of enemies, it would be a betrayal of him as to his being a Mormon elder. He therefore retired to a densely wooded section of the country and, stripping off these garments, rolled them up and climbed a tree and tied them securely....But approaching the neighborhood of Kane Creek where the elders were reported to be killed, the railroad passes over a bit of trestle work over a very deep and quite large ravine, and near the middle of this trestle work he observed three men approaching from the other side, guns in hand. There was nothing left to do than to go right on.
These men proved to be members of the mountain guard watching for me. On meeting Elder Robinson they questioned him as to where he came from and what his purpose was, and when he told them that he was looking for a job cotton picking they laughed saying, "A damn fine cotton picker you would be. Look at your hands." And, of course, as Elder Robinson had not engaged in physical labor, his hands were white and soft, not at all characteristic of cotton pickers. He then told them of having been sick for sometime, and that accounted for his pallor in his face and hands and that he was just now beginning to get about and was now strong enough to begin cotton picking.
Hence he was in search of that job. They invited him to sit down while they thought things over. No sooner did he do that when one of the three grabbed his shirt by the collar and tore it so as to expose his body, but they found no garments incriminating him as to his Mormonism and finally allowed him to pass.[8]
Did Joseph and the others remove their sacred garments in order to avoid being identified as polygamists? There is no documentation that ties the wearing of garments to the practice of polygamy. It was not required that one practice polygamy in order to receive the endowment. In the case of Joseph Smith, he was easily identifiable whether or not he was wearing his garments. Removal of his garments would certainly have made no difference in his being identified and taken to Carthage.
According to the accounts of both John Taylor and Willard Richards—the two eyewitnesses who survived the mob's attack on Carthage jail—Joseph Smith's final words were "O Lord, my God!"
The account in the official History of the Church records:
Joseph, seeing there was no safety in the room, and no doubt thinking that it would save the lives of his brethren in the room if he could get out, turned calmly from the door, dropped his pistol on the floor and sprang into the window when two balls pierced him from the door, and one entered his right breast from without, and he fell outward into the hands of his murderers, exclaiming. "O Lord, my God!"[9]
John Taylor reported:
Hyrum was shot first and fell calmly, exclaiming: I am a dead man! Joseph leaped from the window, and was shot dead in the attempt, exclaiming: O Lord my God! They were both shot after they were dead, in a brutal manner, and both received four balls. (D&C 135:1)
Willard Richards' testimony was that
two balls pierced [Joseph] from the door, and one entered his right breast from without, and he fell outward, exclaiming, "Oh Lord, my God!" As his feet went out of the window my head went in, the balls whistling all around. He fell on his left side a dead man.[10]
Those who knew Joseph Smith believed that his use of the phrase "O Lord, my God!" was an attempt to save his life and the life of his friends by calling out to Freemasons in the mob. (Joseph and the other Mormons in the jail were Masons, Joseph himself having been initiated on 15 March 1842.)
Among the brotherhood of Freemasons, there is the Grand Hailing Sign of Distress: "Oh Lord, my God, is there no help for the widow's son?" According to Masonic code, any Mason who hears another Mason utter the Grand Hailing Sign must come to his aid.
Most adult men in Hancock County, Illinois, were Masons, and there were Masons in the mob that attacked the jail. If Joseph was attempting to give the Grand Hailing Sign, they would have been obligated to stop their attack and defend Joseph, Hyrum, John Taylor, and Willard Richards.[11]
John Taylor, a Master Mason himself, wrote:
...[T]hese two innocent men [Joseph and Hyrum] were confined in jail for a supposed crime, deprived of any weapons to defend themselves: had the pledged faith of the State of Illinois, by Gov. Ford, for their protection, and were then shot to death, while, with uplifted hands they gave such signs of distress as would have commanded the interposition and benevolence of Savages or Pagans. They were both Masons in good standing. Ye brethren of "the mystic tie" [Masonry] what think ye! Where is our good Master Joseph and Hyrum? Is there a pagan, heathen, or savage nation on the globe that would not be moved on this great occasion, as the trees of the forest are moved by a mighty wind? Joseph's last exclamation was "O Lord my God!"
If one of these murderers, their abettors or accessories before or after the fact, are suffered to cumber the earth, without being dealt with according to law, what is life worth, and what is the benefit of laws? and more than all, what is the use of institutions which savages would honor, where civilized beings murder without cause or provocation?[12]
According to Heber C. Kimball:
Masons, it is said, were even among the mob that murdered Joseph and Hyrum in Carthage jail. Joseph, leaping the fatal window, gave the Masonic signal of distress. The answer was the roar of his murderers' muskets.[13]
Zina D. H. Young wrote in 1878:
I am the daughter of a Master Mason [Heber C. Kimball]! I am the widow of a Master Mason [Joseph Smith] who, when leaping from the window of Carthage jail pierced with bullets, made the Masonic sign of distress; but...those signs were not heeded.[14]
From the above it appears the last words of Joseph Smith were believed by at least some people who knew him to be the Masonic cry of distress.
One theory about the martyrdom of Joseph and Hyrum Smith is that they were killed by John Taylor and Willard Richards, who were acting under the orders of Brigham Young. Those advancing this theory rely on their interpretation of evidence currently available about the martyrdom scene. However, this interpretation is inconsistent with widely accepted interpretations by most scholars and researchers. There are three primary reasons why this theory is untenable: (1) currently available evidence, (2) the relationship between Joseph Smith and other Church leaders, and (3) the evidence of the actual assassins.
Little physical evidence currently exists for what happened in the Carthage Jail. In the jail itself, "the only physical evidence of the shooting of Joseph and Hyrum Smith that still remains at Carthage Jail are two bullet holes through the door of the jailer’s bedroom." We also have the clothing Hyrum wore when he was killed and the pocket watch he was carrying.[15] Thus, everything else is based on witness descriptions and later recollections or renderings of the physical scene. We have two eyewitness testimonies of what occurred inside the room, and another eyewitness testimony of what occurred outside the jail.[16] Their testimonies, currently existing physical evidence, and later recollections and renderings substantiate the accuracy of John Taylor's and Willard Richards' accounts. In-depth analyses are available in BYU Studies, Mormon Historical Studies, and Journal of Mormon History.[17]
In addition to current available evidence, proponents of this theory have to account for the relationship between Joseph and those closest to him, including Brigham Young, John Taylor, and Willard Richards. These leaders repeatedly testified of their love for Joseph and their despair that he was martyred. After the martyrdom, John Taylor wrote, "O give me back my Prophet dear, / And Patriarch, O give them back."[18] At a Church conference shortly after Joseph's death, Brigham Young said, "I feel to want to weep for 30 days." He also addressed "rumors that Joseph and Hyrum were not the only leaders targeted by anti-Mormon enemies: 'I don’t know whe[the]r theyll take my life,' he commented, and he confessed that he did not care, for 'I want to be with the man I love.'"[19]
Any theory purporting that these leaders killed Joseph has to account for the abundant evidence of their love for Joseph. Thus, as noted by one observer, this theory has "a gaping hole . . . the question of motive for Willard Richards and John Taylor killing Joseph and Hyrum. Anyone . . . might necessarily wonder why would Richards and Taylor want to kill Joseph and Hyrum? They might also ask whether there is any evidence to suggest that they believed they should do that."[20] Contrary to the motive proposed by those who theorize that Taylor and Richards killed Joseph and Hyrum, we have substantial evidence that the martyrdom was carried out for the mob's own political and religious reasons. This has been documented thoroughly by historian Joseph I. Bentley in BYU Studies.[21]
Video by The Interpreter Foundation.
Finally, any theory about the martyrdom of Joseph and Hyrum has to account for the evidence of the actual assassins. First, the actual assassins proclaimed themselves as having committed the act, as explained by historian Alex Smith:
In the Warsaw Signal, editor Thomas Sharp publishes in the 10 July issue of 1844, an astonishing editorial titled "The Act and the Apology." A spoiler alert: there’s not much apology in it. It’s mostly a justification of why we did this, and I believe in many ways it stands unparalleled in American history as a written explanation for why a community deemed vigilantism necessary. It’s basically saying, had you been us, you would have killed him too.[22]
More evidence of the actual assassins comes from an 1845 trial. Nine men were charged with committing the murder of Joseph and Hyrum, and a trial was held. As explained by Dallin H. Oaks, who researched the trial:
There was ample evidence to convict all nine of the defendants. They were all present. They helped plan and bring the thing about and later bragged about it—ample evidence to convict them. But they were all found not guilty. It was a clear case where the law was against the defendants, but the facts of the case were approved by the jury. In other words, the jury wouldn’t convict someone of an obvious crime when the result of that crime was what the jurors desired. That was known as "jury nullification."…
Something that a principal defense attorney argued to the jury when all the evidence was in [was] he said to the jury, essentially, these men are not guilty because they expressed the community desire to be rid of this man. That’s jury nullification in its rankest description.[23]
The trial and evidence is explored in detail in the book Carthage Conspiracy: The Trial of the Accused Assassins of Joseph Smith.[24]
Key sources |
|
Wiki links |
|
FAIR links |
|
Online |
|
Video |
Load video YouTube YouTube might collect personal data. Privacy Policy Load video YouTube YouTube might collect personal data. Privacy Policy Load video YouTube YouTube might collect personal data. Privacy Policy Load video YouTube YouTube might collect personal data. Privacy Policy Load video YouTube YouTube might collect personal data. Privacy Policy |
Print |
|
Navigators |
Critical sources |
|
Life and Character |
|
Youth |
|
Revelations and the Church |
|
Prophetic Statements |
|
Society |
|
Plural marriage (polygamy) |
|
Death |
An examination of the historical records shows that Joseph was well aware of his fate and faced it head-on as a willing martyr. His death marked a fulfillment of his own prophetic words that appeared as his last narrative in the History of the Church on Saturday June 22, 1844. He said:
I told Stephen Markham that if I and Hyrum were ever taken again we should be massacred, or I was not a prophet of God.[1]:546
Webster's Dictionary provides the following definitions of the word "martyr":
- a person who voluntarily suffers death as the penalty of witnessing to and refusing to renounce a religion
- a person who sacrifices something of great value and especially life itself for the sake of principle
Based upon this definition, we examine whether or not Joseph Smith qualifies as a "martyr."
Joseph was a willing and innocent sacrifice on behalf of his people. He anticipated his death. Wilford Woodruff recorded Joseph's words in 1843 relative to his sacrifice:
I understand my mishion [sic] & business. God Almighty is my shield.... I shall not be sacrafised [sic] untill [sic] my time comes. Then I shall be offered freely.[2]
Similarly in his speech to the Nauvoo Legion on June 18, 1844:
I do not regard my own life. I am ready to be offered a sacrifice for this people; for what can our enemies do? Only kill the body, and their power is then at an end. Stand firm, my friends; never flinch. Do not seek to save your lives, for he that is afraid to die for the truth, will lose eternal life.... God has tried you. You are a good people; therefore I love you with all my heart. Greater love hath no man than that he should lay down his life for his friends. You have stood by me in the hour of trouble, and I am willing to sacrifice my life for your preservation.[1]
Hyrum and Helen Andrus describe Joseph's willingness and those who pleaded with him to not surrender:
As Joseph contemplated the scene, he could picture in his mind the militia overrunning Nauvoo and committing the same autracites as were acted upon the Saints in Missouri. Thus on Monday the 24th of June, Joseph expressed his resolution as "hundreds gathered before the Mansion House early in the morning. In their midst, with head erect, towering above the rest, the Prophet stood gazing alternately on the devoted city and its much loved citizens. He listened to the entreaties of the throng not to give himself up or he would be murdered. A few brave-hearted men proposed to escort him to the West. Others, up north would have him go, while a fearless tar (sailor) proffered him a safe passage on a steamboat to whither he would go. A smile of approbation lit up the Seer's countenance. His lovely boys, hanging on to his skirts, urged on the suite and cried, "Father, O Father don't go to Carthage. They will kill you." Not least impressive were the pleadings of his mother: "My son, my son, can you leave me without promising to return? Some forty times before have I seen you from me dragged, but never before without saying you would return; what say you now, my son?" He stood erect, like a beacon among roaring breakers, his gigantic mind grasping still higher. The fire flashed in his eye. With hand uplifted on high, he spoke, "My friends, nay, dearer still, my brethren, I love you. I love the city of Nauvoo too well to save my life at your expense. If I go not to them, they will come and act out the horrid Missouri scenes in Nauvoo. I may prevent it. I fear not death. My work is well nigh done. Keep the faith and I will die for Nauvoo."[3]
A guard from Carthage warned Joseph in Nauvoo before he left:
"If you go there they will kill you." "I know it, but I am going. I am going to give myself for the people, to save them" Joseph said.[4]
Joseph told the company who were with him:
I am going like a lamb to the slaughter, but I am calm as a summer's morning. I have a conscience void of offense toward God and toward all men. If they take my life I shall die an innocent man, and my blood shall cry from the ground for vengeance, and it shall be said of me "He was murdered in cold blood!" [1]:6:555
On June 24, after Joseph's last visit with his family before going to Carthage, William Clayton writes:
He appeared to feel solemn & though[t]ful, and from expressions made to several individuals, he expects nothing but to be massacred. This he expressed before he returned from over the river but their appearing no alternative but he must either give himself up or the City be massacred by a lawless mob under the sanction of the Governor.[5]
In Joseph Smith's letter to Emma written from the Carthage Jail, on the final day of his life, he wrote:
"Dear Emma, I am very much resigned to my lot, knowing I am justified, and have done the best that could be done. Give my love to the children and all my friends."[1]:605
Joseph was, and always had been, willing to die for his faith, his God, and his people. Danel Bachman, illustrating this willingness, cited an 1838 incident when Joseph and Hyrum were in the hands of their enemies and were sentenced to be executed. Did he resist? No! Joseph, speaking of his feelings at the time said:
As far as I was concerned, I felt perfectly calm, and resigned to the will of my heavenly Father.... And notwithstanding that every avenue of escape seemed to be entirely closed, and death stared me in the face, and that my destruction was determined upon, as far as man was concerned; yet, from my first entrance into the camp, I felt an assurance, that I with my brethren and our families should be delivered. Yes, that still small voice, which has so often whispered consolation to my soul, in the depth of sorrow and distress, bade me be of good cheer, and promised deliverance.
Hyrum said of the event:
I thank God that I felt a determination to die, rather than deny the things which my eyes had seen, which my hands had handled, and which I had borne testimony to, wherever my lot had been cast; and I can assure my beloved brethren that I was enabled to bear as strong a testimony, when nothing but death presented itself, as ever I did in my life. My confidence in God was likewise unshaken."[6]
Joseph's history, words, and actions go contrary to many of his critics' picture of cowardliness. Joseph was well aware that the anti-Mormon sentiment was to "exterminate, utterly exterminate the wicked and abominable Mormon leaders, the authors of [their] troubles."[1]:5:456
Fawn Brodie claimed that Joseph Smith was panicking at Carthage Jail, and wrote an order to Jonathan Dunham (head of the Nauvoo legion), telling him to attack the jail and "save him at all costs" [7]
There is little good evidence from the extant documents that Joseph attempted to have the Nauvoo Legion rescue him. By contrast, he repeatedly ordered the militia to stay home and his followers to avoid assembling. He repeatedly expressed resignation as to his fate, and just prior to his martyrdom was seeking to add more legal help to his hearing two days distant—a strange choice if he expected to be liberated by the militia.
That Dunham would receive orders from Joseph and refuse to follow them seems incredible. It would also be strange for Stout to be the only primary source to learn of such orders. Why would Dunham tell anyone that he had refused an order from the prophet? Why would he tell Stout, a fierce supporter of Joseph? Why did others not hear of this and report it? Why was Dunham not blamed by other LDS members later?
Stenhouse tells the story, and claims that the order was found discarded on the ground—again, this seems incredible. Why would Dunham dispose of such an incriminating bit of evidence so carelessly? If it was found, why did Brigham Young or other Church leaders never hear of, mention, or save it? The entire tale sounds more like gossip or grumbling among a few who felt that the Mormons militia could have rescued Joseph if given the chance.
Dunham's death was reported in William Clayton's diary as follows:
Daniel Spencer has returned from the West. He brings word that Brother Jonathan Dunham died of a fever.[8]
Thus, the attribution of Dunham's death to suicide occurs later. Even if the suicide claim is accepted, Oliver Huntington's witness says that it was because Dunham felt guilty for being unable to fortify Nauvoo adequately before Joseph went to Carthage for the last time.
The weight of evidence cannot, at present, sustain the claim that Joseph commanded the Nauvoo Legion to come rescue him.[9] Errors, miscitation of sources, and typographical problems have further clouded this issue.
The first derives from Fawn Brodie (1945):
Other authors have followed Brodie. Abanes (One Nation Under Gods), for example, merely quotes Brodie as his source. Denton simply repeats the claim without acknowledging Brodie as the source.
Brodie's evidence derives from two sources:
Brodie says that Stout's story "is confirmed" by Stenhouse, but Stenhouse mentions no names.[10]:n.94
The second evidential stream draws on the first, but adds a new wrinkle. This wrinkle is one of the Hofmann forgeries.[11] Mark Hofmann forged the supposed letter from Joseph to Dunham, and it was published in a collection of Joseph's personal writings before the forgery was discovered.
Despite the fact that the document is a forgery, some authors have continued to use it. For example, D. Michael Quinn used it as evidence as late as 1994, and cites the Jessee transcript of the letter (cited above):
The morning of 27 July, Smith sent an order (in his own handwriting) to Major-General Jonathan Dunham to lead the Nauvoo Legion in a military attack on Carthage "immediately" to free the prisoners. Dunham realized that such an assault by the Nauvoo Legion would result in two blood baths—one in Carthage and another when anti-Mormons (and probably the Illinois militia) retaliated by laying siege to Nauvoo for insurrection. To avoid civil war and the destruction of Nauvoo's population, Dunham refused to obey the order and did not notify Smith of his decision. One of his lieutenants, a former Danite, later complained that Dunham "did not let a single mortal know that he had received such orders."
We note too that the History of the Church citation is also in error; Quinn transposed two numbers; the correct citation is 6:592. Despite this claim, there is no mention in History of the Church that Joseph wrote a letter to Dunham urging him to come to their rescue. Joseph wrote several known letters to Dunham, none of which supports Quinn's claim. The History of the Church entry reads:
"Willard Richards made copies of the orders of Joseph Smith as Mayor to Marshal John P. Greene, and as Lieut.-General to Major-General Jonathan Dunham."
These are clearly the letters referred to earlier in the History of the Church (see 6:493), which say nothing about rescuing the prisoners at Carthage.
Quinn goes on to claim that:
However, another former Danite took self-inflicted retribution for the death of Joseph Smith. When Nauvoo Mormons learned that Jonathan Dunham had ignored the prophet's direct order to lead the Nauvoo Legion in a rescue at Carthage Jail, some called him a "coward and traitor." Others dismissed him as a "fool and idiot."....[12]:179
He here uses the same citation as before: the Jesse volume, with its forged Hofmann document.
In 1995, Quinn wrote a letter in which he acknowledged his reference to the forged document and included and explanation:
While vacationing in California during January, I received a telephone call informing me that my newly published book Mormon Hierarchy had cited a Hoffman-forged letter to Jonathan Dunham in the source notes. I'll spare you my immediate reaction, but it was stronger than "Oh hell!"....
The only parts of the Dunham letter I used were the variant date (a day later than History of the Church) and the word "immediately," but during my rushed revision of this passage I mistyped the month in my narrative. I should have caught my misstatement that Joseph Smith wrote these orders a month after his June death, but I never saw that error. Nor did I see the typographical error of transposing the page-number citation in History of the Church for the letter.[13]
Quinn continues to insist on his misreading of the History of the Church entry (see discussion above), only correcting his typographical error in the citation (6:592 instead of 6:529).
Quinn ignores that he also claimed (without evidence save from the forgery) that the writing was "in his [Joseph's] own handwriting."

Quinn went on to claim that he could only locate this information in Silitoe and Roberts' 1988 volume Salamander. While the information is available in Salamander (see pp. 110, 132, 282, 547, and plate 37), this was not the only source available. The letter's forged status was also discussed in Dialogue 21/4 (Winter 1988): 170. BYU Studies included a long list of forged documents and other material related to the Hofmann forgeries in 1989, including the Dunham letter.[14]. Curtis Bench produced an errata sheet for Dean Jesse's book Personal Writings of Joseph Smith in 1986-1987.[15]
Quinn made corrections for the 1997 printing of Origins of Power. However, his publisher issued the New Mormon Studies CD-ROM in 1998, but still included Quinn's erroneous 1994 version in this digital product.
Quinn tries to provide extra proof by writing that:
Later general authority Seymour B. Young (who had survived the Haun's Mill massacre) recorded a different story he learned from another former Danite. Ever since the martyrdom, Dunham "seemed to grieve over the matter" of not rescuing the prisoners at Carthage, and the anniversary of the prophet's death pushed him into despair. A month later he persuaded "a friendly Indian" (Dana) "to kill and bury him."[12]:179
For this claim, Quinn appeals again to Stenhouse (who, as noted above, mentioned no names and could have had no personal knowledge of these events), and to an Oliver B. Huntington statement, in Seymour B. Young diary, 23 May 1903, LDS archives. But, this supposed confirmation turns out to be nothing of the sort. Dean Jessee wrote, in a review of Quinn's work that
In his treatment of Joseph Smith's death, Quinn refers to the statement by Allen Stout that Joseph, in Carthage Jail, had ordered Jonathan Dunham, commander of the Nauvoo Legion, to bring the legion and rescue him; and that Dunham did not respond (p. 141). Quinn quotes Seymour Young's 1903 conversation with Oliver Huntington, reporting that Dunham "seemed to grieve over the matter" of failing to rescue Joseph; depressed, Dunham persuaded a friendly Indian to kill and bury him (pp. 179-80). But Quinn has altered the Young conversation with Huntington to support Stout's story that Joseph had sent for the Nauvoo Legion. According to Young, Huntington informed him that, in the spring of 1844, Joseph told Dunham to fortify Nauvoo so the Saints could make a stand against their enemies. Dunham's depression after the martyrdom was over his failure to complete the fortification; he felt that had he done so, the Prophet might not have had to go to Carthage in the first place.[16]:167
Jessee makes no mention of Quinn's further difficulties in using the forged Hofmann document years after its status as a fraud was revealed. Thus, the case for Joseph's order to Dunham rests only on Stout's account. Stenhouse mentions the story, but he was in England at the time. He could have had no independent confirmation.
This does not stop Quinn from later, in his timeline, acting as if his entire scenario is well-proven:
28 July. Jonathan Dunham, despondent about disobeying Smith's orders to rescue him from jail, commits suicide. Later disclosures indicate that Dunham, who was a captain of Nauvoo's police, major-general of the Nauvoo Legion, and a Council of Fifty member, accomplished the suicide by asking a native American friend (Lewis Dana, fellow member of the Fifty) to "kill and bury him."[12]:652
No references are provided, a deficiency which reviewers have noted.[17]
June 17, 1844: Joseph issued three letters of instruction which impacted Dunham. The first was to John P. Greene, marshal of the city:
SIR.—Complaint having been made to me on oath that a mob is collecting at sundry points to make an attack on this city, you will therefore take such measures as shall be necessary to preserve the peace of said city according to the provisions of the charter and the laws of the state; and with the police and the Legion, see that no violent set is committed. General Dunham is hereby instructed to act with the Marshal in keeping the peace, according to law.
The second two letters addressed Dunham directly:
Complaint having been made on oath that a mob is preparing to make an attack upon this city and citizens of Nauvoo, and having directed the Marshal to keep the peace, you are hereby commanded to order the Nauvoo Legion to be in readiness to assist said Marshal in keeping the peace, and doing whatever may be necessary to preserve the dignity of the state and city....
You are hereby instructed to execute all orders of the Marshal, and perform all services with as little noise and confusion as possible, and take every precaution to prevent groups of citizens, &c., from gathering on the bank of the river, on the landing of boats or otherwise, and allay every cause and pretext of excitement as well as suspicion, and let your operations be efficient and decided.[1]:493
On the 20th Joseph said, "I went with my staff and Major-General Dunham to the prairie, to view the situation of the ground, and to devise plans for the defense of the city, and select the proper locations to meet the mob, and made arrangements for provisions for the city, instructing my agent to pledge my farms for the purpose."[1]:528
Joseph wrote to Dunham,
You will proceed without delay, with the assistance of the Nauvoo Legion, to prepare the background [Eastern part] of said city for defense against an invasion by mobs, cause the Legion to be furnished with tents, and make your encampment in the vicinity of your labor.[1]:532
Joseph instructed Dunham to comply with the governor's order for the Nauvoo Legion to return state arms.[1]:556 The next day, Joseph and Hyrum surrendered themselves and went to Carthage.
Joseph was safely away in Iowa with Hyrum. He returned to surrender himself to the Illinois governor, Thomas Ford, after being appealed to by Emma and others. Emma reported that Joseph said, "I will die before I will be called a coward."[18]
Joseph also remarked that "If my life is of no value to my friends [those in Nauvoo who were urging him to return for fear of the mob] it is of none to myself....if they had let me alone there would have been no bloodshed but now I expect to be butchered. Hyrum likewise remarked that "We had better go back and die like men." And, on the way out of Nauvoo to Carthage, Joseph was reported to say, "I go like a lamb to the slaughter."[19]
Joseph wrote,
There was a little mutiny among the "Carthage Greys"; but I think the Gov. has & will succeed in enforcing the laws. I do hope the people of Nauvoo will continue placid pacific & prayerful.
N.B. Governor Ford has just concluded to send some of his malitia to Nauvoo to protect the citizens, & I wish that I they may be kindly treated. They will co-ope=rate with the police to keep the peace
of the cityThe Governors orders will be read in hearing of the police & officers of the Legion, as I suppose.[20]
Joseph hopes Mormons will remain "placid, pacific, and prayerful." He notes that the state militia will keep peace in Nauvoo—a sure obstacle to any attempt to call out the militia.
...I want you to tell Bro Dunham to instruct the people to stay at home and attend to their own business and let there be no groups or gathering together unless by permission of the Gov— they are called together to receive communications from the Gov— which would please our people, but let the Gov. direct. —Bro Dunham of course, will obey the orders of the Government officers, and render them the assistance they require....I am very much resigned to my lot knowing I am Justified and have done the best that could be done give my love to the children[21]
Joseph is here forbidding assembly of the people, a necessary prelude to any attempt to rescue him or Hyrum.
Joseph's last known letter was to an attorney he wished to add to his legal defense:
Myself and brother Hyrum are in Jail on [a] charge of Treason, to come up for examination on Saturday morning 29th inst. and we request your professional services at that time, on our defence without fail....P.S. There is no
groundof action, for we have not been guilty of any crime; neither is there any just cause of suspicion against uswhen facts are shownbut certain circumstances make your attendance very necessary.[22]
Critical sources |
|
D. Michael Quinn makes the following claim:
Mar 21,1858 - Brigham Young tells this special conference that Joseph Smith disobeyed revelation by returning to Nauvoo to stand trial, that the church’s founding prophet lost Spirit of God the last days of his life, and died as unnecessary martyr. He published this talk as pamphlet. [23]
Joseph's mind was made up. Vilate Kimball described Joseph's pause as his stopping to compose his mind and getting the will of the Lord concerning him, that will of course being that he should return and face his fate. "Their giveing [sic] themselves up," says Vilate, " is all that will save our city from destruction."[24] Thus, although Joseph disregarded the Lord's warning to leave, he sought the Lord's will concerning his decision to return in order to save Nauvoo. There is no indication that he sinned or lost the Lord's guidance by doing so.
Danel Bachman discussed this issue at the Joseph Smith Symposium in 1992:
Vilate Kimball adds a unique perspective to the Prophet’s return across the Mississippi on 24 June. Some accounts say that Joseph had a revelation directing him to head west (HC 6:545-46). But Vilate wrote to her husband that, "Joseph went over the river out of the United States, and there stoped [sic] and composed his mind, and got the will of the Lord concerning him, and that was, that he should return and give himself up for trial" (Esplin 235). Was there a revelation? Were there two revelations? No one knows, but I do not doubt the possibility.[25]
Joseph no doubt would have sought the Lord's guidance before returning to Nauvoo. The Church held a conference in Boston shortly after Joseph's death, with much of the Quorum of the Twelve being present.[26] Elder Woodruff arrived in Boston on July 10th, and Orson Hyde arrived on the 18th. According to Elder Woodruff, Elder Hyde "had advertised to Preach upon the murder of Joseph and Hyram Smith."[27] Woodruff provided in his journal a synopsis of Elder Hyde's comments,
A word about Br Joseph being killed. Some have thought he could not be killed. But the Lord never said so neither did Joseph say so. So did Peter say to Jesus when he told him that he would be slain or offered, far be it from thee. This shall not come upon thee. Jesus said get the behind me Satan. Thou savoreth not the things that be of God but of men.
In the first instance The Prophet crossed the river to Iowa & while there he inquired of the Lord what he should do and the Lord told him to return and give himself up. He appeared to be aware that he would be slain.[28]
From History of the Church, Vol 6, Ch. XXIX:
Saturday, June 11 [22], 1844.--About 9 p. m. Hyrum came out of the Mansion and gave his hand to Reynolds Cahoon, at the same time saying, "A company of men are seeking to kill my brother Joseph, and the Lord has warned him to flee to the Rocky Mountains to save his life. Goodbye, Brother Cahoon, we shall see you again." In a few minutes afterwards Joseph came from his family. His tears were flowing fast. Be held a handkerchief to his face, and followed after Brother Hyrum without uttering a word. (emphasis added)
According to this, Hyrum said that the Lord warned Joseph to flee to the Rocky Mountains. When Joseph ultimately turned back toward Nauvoo, he was turning away from safety toward likely death.
Brigham Young expressed his view on this action. From the journal of Charles Walker:
21 March 1858
Bro. Brigham spoke a little on the rise and persecution of the Church said that if Bro. Joseph Smith had been led by the Spirit he had, he would never given himself up and gone to Carthage but he would have gone right to these mountains and would have been alive today to lead this people. Said the sheep must follow the shepherd not the shepherd follow the sheep. Said it was not policy to shed the blood of our enemies and was better to leave our homes than to be driven from them spoke of us burning our houses. . . said he was going to send 500 families across the Desert to the White Mountains as soon as possible. Said some might think he was mistaken says he is the voice of God to this people and their salvation and you can do as you darn please but I am going there when the time comes. (emphasis added)
—Charles Walker Journal p3[29]
Based upon the Brigham Young source shown above, D. Michael Quinn claims:
Examining the Brigham Young quote that Quinn used as his source, it is clear that Brigham believed that if Joseph had "been led by the Spirit he had," that he would have not returned to Nauvoo and that his life would have been spared. Thus Brigham felt that Joseph's death was not necessary. This could be used to support Quinn's claims #1 and #3.
Quinn's claim #2, that Joseph "lost the Spirit of God the last days of his life," is clearly not supported by Brigham's statement. In fact, it states quite the opposite—that if Joseph "had been led by the Spirit he had," that he would not have returned to Nauvoo and ultimately been killed.
Why did Joseph turn around and return to Nauvoo? In response to the accusations of abandonment from Emma and some in his party, Joseph said,
"'If my life is of no value to my friends it is of none to myself.' Joseph said to Rockwell, 'What shall I do?' Rockwell replied, 'You are the oldest and ought to know best; and as you make your bed, I will lie with you.' Joseph then turned to Hyrum, who was talking with [Reynolds] Cahoon, and said, 'Brother Hyrum, you are the oldest, what shall we do?' Hyrum said, 'Let us go back and give ourselves up, and see the thing out.' After studying a few moments, Joseph said, 'If you go back I will go with you, but we shall be butchered.' Hyrum said, 'No, no; let us go back and put our trust in God, and we shall not be harmed. The Lord is in it. If we live or have to die, we will be reconciled to our fate.' After a short pause, Joseph told Cahoon to request Captain Daniel C. Davis to have his boat ready at half-past five to cross them over the river."[30]
Non-Mormon Colonel John Hay, an American poet and statesman, recorded the day's details leading up to the murder, shedding light on the mood of the mob that infamous day. He wrote:
[The mobsters] followed their leaders off on the road to Carthage, with rather vague intentions. They were annoyed at the prospect of their picnic coming so readily to a close, at losing the fun of sacking Nauvoo, at having to go home without material for a single romance... These trudged along under the fierce summer sun of the prairies towards the town where the cause of all the trouble and confusion of the last few years awaited them.
The farther they walked the more the idea impressed itself upon them that now was the time to finish the matter totally. The unavowed design of the leaders communicated itself magnetically to the men, until the entire company became fused into one mass of bloodthirsty energy...
...As the avengers came in sight of the mean-looking building that held their prey, the sleeping tiger that lurks in every human heart sprang up in theirs, and they quickened their pace to a run. There was no need of orders,-no possibility of checking them now. The guards were hustled away from the door, good-naturedly resisting until they were carefully disarmed.162
Interjecting into Hay's narrative, the view from inside the jail finds the mob rushing up the stairs to the room where Joseph and his friends were. It was "at this point, Joseph sprang to his coat for his six-shooter, Hyrum for his single barrel, Taylor for Markham's large hickory cane, and Dr. Richards for Taylor's cane. All sprang against the door, the balls whistled up the stairway, and in an instant one came through the door...Joseph Smith, John Taylor and Dr. Richards sprang to the left of the door, and tried to knock aside the guns of the ruffians...Joseph, seeing there was no safety in the room, and no doubt thinking that it would save the lives of his brethren in the room if he could get out, turned calmly from the door, dropped his pistol on the floor and sprang into the window when two balls pierced him from the door, and one entered his right breast from without, and he fell outward into the hands of his murderers, exclaiming. 'O Lord, my God!'"[31]
The idea that Joseph tried to escape through the window to save the lives of Richards and Taylor is in harmony with one of the reasons he went to Carthage to begin with.[32]
The historical account reads that "Dr. Richards' escape was miraculous; he being a very large man, and in the midst of a shower of balls, yet he stood unscathed, with the exception of a ball which grazed the tip end of the lower part of his left ear. His escape fulfilled literally a prophecy which Joseph made over a year previously, that the time would come that the balls would fly around him like hail, and he should see his friends fall on the right and on the left, but that there should not be a hole in his garment."[33]
Mr. Hay continuing with his narrative writes:
Joe Smith died bravely...after he half leaped, half fell, into the jail yard below. With his last dying energies he gathered himself up, and leaned in a sitting posture against the rude stone well-curb. His stricken condition, his vague wandering glances, excited no pity in the mob thirsting for his life.
A squad of Missourians who were standing by the fence leveled their pieces at him, and, before they could see him again for the smoke they made, Joe Smith was dead.
The moment the work was done, the calmness of horror succeeded the fever of fanatical rage. The assassins hurried away from the jail, and took the road to Warsaw in silence and haste. They went home at a killing pace over the wide, dusty prairie.
Life and Character |
|
Youth |
|
Revelations and the Church |
|
Prophetic Statements |
|
Society |
|
Plural marriage (polygamy) |
|
Death |
| Related articles: | John C. Bennett and plural marriage at Nauvoo Summary: Mountebank, deceiver, and charmer, John C. Bennett's arrival at Nauvoo and his interactions with the Saints and Joseph would have a lasting impact that led indirectly to Joseph's death. |
| Nauvoo city charter Summary: Follow this to learn about historical and political events that preceded the Nauvoo Expositor issue. The powers granted Nauvoo were not seized by the Saints; they were granted lawfully, and could have been removed lawfully by the legislature. |
It is claimed by one critic of the Church that Joseph "could not allow the Expositor to publish the secret international negotiations masterminded by Mormonism’s earthly king." [1] Another claimed that "When the Laws (with others) purchased a printing press in an attempt to hold Joseph Smith accountable for his polygamy (which he was denying publicly), Joseph ordered the destruction of the printing press, which was both a violation of the 1st Amendment, and which ultimately led to Joseph’s assassination." [2]
The Expositor incident led directly to the murder of Joseph and Hyrum, but it was preceded by a long period of non-Mormon distrust of Joseph Smith, and attempts to extradite him on questionable basis.
The destruction of the Expositor issue was legal; it was not legal to have destroyed the type, but this was a civil matter, not a criminal one, and one for which Joseph was willing to pay a fine if imposed.
Joseph seems to have believed—or, his followers believed after his death—that the decision, while 'unwise' for Joseph, may have been in the Saints' interest to have Joseph killed. For a time, this diffused much of the tension and may have prevented an outbreak of generalized violence against the Saints, as occurred in Missouri.
It is claimed that "When the Laws (with others) purchased a printing press in an attempt to hold Joseph Smith accountable for his polygamy (which he was denying publicly), Joseph ordered the destruction of the printing press, which was both a violation of the 1st Amendment, and which ultimately led to Joseph’s assassination." [3]
The destruction of the Expositor issue (i.e., the paper itself) was legal; it was not legal to have destroyed the type, but this was a civil matter, not a criminal one, and one for which Joseph was willing to pay a fine if imposed.
Joseph did not unilaterally order the action against the Expositor—it was the Nauvoo City Council (which included non-Mormons) which reached the unanimous decision. Having reached that decision, Joseph Smith then issued an order, as mayor, to carry out the Council's decision. As described in the Church's 2011 Priesthood/Relief Society manual:
On June 10, 1844, Joseph Smith, who was the mayor of Nauvoo, and the Nauvoo city council ordered the destruction of the Nauvoo Expositor and the press on which it was printed. [4]
History of the Church also describes this event [5]:
I [Joseph Smith] immediately ordered the Marshal to destroy it [the Nauvoo Expositor] without delay, and at the same time issued an order to Jonathan Dunham, acting Major-General of the Nauvoo Legion, to assist the Marshal with the Legion, if called upon so to do." [6]
The First Amendment is irrelevant to this discussion. In 1844, the First Amendment only applied to federal law; it had no application to state or local law until the passing of the Fourteenth Amendment after the Civil War.
Critical sources |
|
A Canadian, William Law joined the Church in 1836 and moved to Nauvoo in 1839. After having lived near Joseph Smith in Nauvoo, William wrote to a friend:
I have carefully watched his movements since I have been here, and I assure you I have found him honest and honourable in all our transactions which have been very considerable. I believe he is an honest upright man, and as to his follies let who ever is guiltless throw the first stone at him, I shant do it.[7]
His non-member son, Richard, later recounted:
About the year 1842, he was present at an interview between his father and the Prophet Joseph. The topic under discussion was the doctrine of plural marriage. William Law, with his arms around the neck of the Prophet, was pleading with him to withdraw the doctrine of plural marriage, which he had at that time commenced to teach to some of the brethren, Mr. Law predicting that if Joseph would abandon the doctrine, 'Mormonism' would, in fifty or one hundred years, dominate the Christian world. Mr. Law pleaded for this with Joseph with tears streaming from his eyes. The Prophet was also in tears, but he informed the gentleman that he could not withdraw the doctrine, for God had commanded him to teach it, and condemnation would come upon him if he was not obedient to the commandment.
During the discussion, Joseph was deeply affected. Mr. Richard S. Law says the interview was a most touching one, and was riveted upon his mind in a manner that has kept it fresh and distinct in his memory, as if it had occurred but yesterday.
Mr. Law also says, that he has no doubt that Joseph believed he had received the doctrine of plural marriage from the Lord. The Prophet's manner being exceedingly earnest, so much so, that Mr. Law was convinced that the Prophet was perfectly sincere in his declaration.[9]
William even decided that Joseph Smith’s opposition to Missouri (and the treatment the Saints had received there) was "unChristian"!
The hostile spirit and conduct manifested by Joseph Smith, and many of his associates towards Missouri . . . are decidedly at variance with the true spirit of Christianity, and should not be encouraged by any people, much less by those professing to be the ministers of the gospel of peace.[11]
William had economic quarrels with Joseph, and was probably too fond of his own financial state, rather than helping the poor of the Church. William and his brother Wilson had bought the higher land on the outskirts of Nauvoo; the Church (through Joseph) owned the land in the river bottom. Joseph declared that new arrivals should purchase lands from the Church (this was in part an effort to help liquidate the Church’s debts), but William objected to this plan as prejudicial to his own financial interests.[12]
William was probably also troubled by the death of his wife and daughter even after Church leaders had prayed for them. Hyrum presented Law and his wife with the revelation on plural marriage. Long after the fact, William reported his reaction:
Hyrum gave it [the revelation] to me in his office, told me to take it home and read it, and then be careful with it, and bring it back again…[My wife Jane] and I were just turned upside down by it…We did not know what to do.[13]
It is not clear whether Jane and William Law were ever sealed. Alexander Neibaur and Hyrum Smith both reported that Joseph told William he could not seal him to Jane because the Lord forbade it; Neibaur indicated that this was because William was "a Adulterous person."[14] There is no evidence of this other than Neibaur's statement however.
In the clash that followed, William began "casting the first stone," at Joseph’s supposed failings, and the man which he had once admired as honourable and without cause for complaint became, in his newspaper, a "demon," a power-mad tyrant, a seducer, and someone who contributed to the early death of young women.
William Law announced he would reconcile only under the condition that Joseph publicly state that the practice of polygamy was "from Hell":
I told him [Sidney] that if they wanted peace they could have it on the following conditions, That Joseph Smith would acknowledge publicly that he had taught and practised the doctrine of plurality of wives, that he brought a revelation supporting the doctrine, and that he should own the whole system (revelation and all) to be from Hell.[15]
Shortly afterward, on 7 June 1844, the first (and only) edition of the Nauvoo Expositor was published. It detailed Joseph’s practice of plural marriage, and charged him with various crimes, labeling him a "blood thirsty and murderous...demon...in human shape" and "a syncophant, whose attempt for power find no parallel in history...one of the blackest and basest scoundrels that has appeared upon the stage of human existence since the days of Nero, and Caligula."[16]
It is claimed that Joseph "could not allow the Expositor to publish the secret international negotiations masterminded by Mormonism’s earthly king." [23]
The reality was that the Joseph and the City Council were concerned that the paper would cause turmoil among the Saints.
One member stated,
Brother Joseph called a meeting at his own house and told us that God showed to him in an open vision in daylight [meaning that this was not something he had just conjured up in dreams of the night] that if he did not destroy that printing press that it would cause the blood of the Saints to flow in the streets and by this was that evil destroyed.[24]
Given Joseph’s numerous presentiments of his own death, it may well be that he knowingly chose this course of action to spare the members’ lives at the cost of his own. Said Joseph to Elizabeth Rollins:
I must seal my testimony with my blood.[25]
And later:
Some has supposed that Br Joseph Could not die but this is a mistake it is true their has been times when I have had the promise of my life to accomplish such & such things, but having accomplish those things I have not at present any lease of my life I am as liable to die as other men.[26]
Bennett’s apostasy caused particular problems because he claimed that the doctrines he was using to seduce women in Nauvoo were the same as those taught privately by Joseph Smith with regard to plural marriage. Thus, Joseph and the Church spent a great deal of time denying Bennett’s charges, while trying to keep plural marriage from becoming common knowledge for fear of the Church’s enemies.
Bennett left the Church and Nauvoo, and spoke widely about the "evils" of the Church and its leaders to non-member audiences. He also wrote a book and made a good deal of money telling stories against the Mormons; he was later to be associated with Sidney Rigdon’s splinter group and the "Strangite" break-off group, but he soon left them as well.
Orson F. Whitney said this about Bennett:
In May, 1842, the treachery and rascality of a man whom the Mormon leader had befriended and loaded with honors, became known to his benefactor. That man was Dr. John C. Bennett, Mayor of Nauvoo, Chancellor of its University, and Major-General of its legion. He had become associated with the Saints soon after their exodus from Missouri. Though a great egotist, he was a man of education, address and ability. That he had little or no principle was not immediately apparent. Considerable of a diplomat and possessing some influence in political circles, he rendered valuable aid in securing the passage by the Illinois Legislature of the act incorporating the city of Nauvoo. Hence the honors bestowed upon him by the Mormon people. Prior to that, and subsequently, he was Quartermaster-General of Illinois. Bennett professed great sympathy for the Saints. He joined the Church and apparently was a sincere convert to the faith.
Governor Thomas Ford, in his history of Illinois, styles Bennett "probably the greatest scamp in the western country." But this was not until long after the Mormons, thrice victimized, had become aware of his villainy.[30]
William Law was Joseph's counselor, but eventually broke with the Prophet and helped publish the Nauvoo Expositor. |
|
Opposed to polygamy, Joseph's counsellor William Law opened a printing press where he planned to expose the teachings he could not accept. The June 7 edition of the Nauvoo Expositor, the first and only edition, included plain accusations against the Prophet. |
|
William Marks related that Joseph’s conversation denouncing plural marriage occurred “three weeks before his death” or around June 6. Perhaps Joseph had such a change of heart during the first week of June, but this seems unlikely and other parts of Marks’ recollection are implausible. |
Critical sources |
|
Life and Character |
|
Youth |
|
Revelations and the Church |
|
Prophetic Statements |
|
Society |
|
Plural marriage (polygamy) |
|
Death |
The Word of Wisdom was enforced differently in the 19th century than today. Observance of the Word of Wisdom has changed over time, due to on-going revelation from modern-day prophets, who put greater emphasis on certain elements of the revelation originally given to Joseph Smith. Early Latter-day Saints were not under the same requirements as today's Saints are.
Latter-Day Saints believe that the Lord reveals his will to men "line upon line, precept upon precept," (Isaiah 28:10,13 and others) and that revelation continues as circumstances change.
As one historian noted:
it appears clear that Joseph Smith never interpreted the [Word of Wisdom] revelation as demanding total abstinence, but stressed moderation and self-control....He had no objections to using tobacco for medicinal purposes. With regard to wine and "strong drink" possibly the most accurate index to the Prophet's position was expressed by Benjamin F. Johnson, who personally knew Joseph: "As a companion, socailly, he was highly endowed; was kind, generous, mirth loving, and a times even convivial. He was partial to a well supplied table and he did not always refuse the wine that maketh the heart glad."[1]
The text of the Word of Wisdom forbids "strong drink" (D&C 89꞉5,7), which some (including Joseph) seem to have interpreted as distilled beverages (hard liquor). Beer, unfermented or lightly fermented wine, and cider were considered "mild drinks" by some (D&C 89꞉17) and therefore acceptable under at least some circumstances (note that verse 17 specifically permits "barley...for mild drinks"). One historian notes that the degree of rigor with which early Saints observed the Word of Wisdom varied:
[23] While the Saints opposed the common use of tea [24] and coffee, it would appear that they had little objection to its occasional use for medicinal purposes. In an age when these items were frequently used as a relief for a wide variety of ailments, it would have been imprudent to have entirely forbidden their use....
[25] The journal of Joseph Smith reveals many instances where Joseph and other Church leaders drank wine and a tolerant attitude towards the consumption of this beverage is particularly noticeable....
[26] Despite the injunction contained in the revelation discouraging the drinking of wine, (except for sacramental purposes) the casual nature of the allusions to this beverage suggest that many Church Authorities did not consider moderate wine drinking in the same category as the use of strong drinks....
Evidence suggests that the drinking of tea, coffee, and liquor was [in the 1830s] in general violation of the principle [of the Word of Wisdom], though exceptions can be found. All of these items were used by the Saints for medicinal purposes. Moderate wine-drinking was evidently acceptable to most Church leaders....[27] In short, it would seem that adherence to the revelation to at least 1839 required Church members to be moderately temperate but certainly [did] not [require] total abstinence....[2]
Liquor in judicious amounts was used as a medicinal substance, and seen as a stimulant or restorative against fatigue. This is why Joseph "investigated the case"--he wished to know if the use had been acceptable or to excess. (In a similar way, a modern-day Church leader who heard that a member was using morphine might investigate to discover if such use is appropriate--e.g., under a doctor's supervision in proper prescribed amounts for a legitimate ailment--or whether they were abusing it to get "high".)
Here's what Joseph said,
The company moved on to Andover, where the Sheriff of Lee County requested lodgings for the night for all the company. I was put up into a room and locked up with Captain Grover. It was reported to me that some of the brethren had been drinking whiskey that day in violation of the Word of Wisdom.
I called the brethren in and investigated the case, and was satisfied that no evil had been done, and gave them a couple of dollars, with directions to replenish the bottle to stimulate them in the fatigues of their sleepless journey.[3]
Critics of the Church who use this quote as evidence that Joseph disregarded the Word of Wisdom also do not inform readers that the complete prohibition on alcohol was a gradual matter, and so Joseph's judgment on the issue was possible (which explains why no one at the time was shocked or outraged by it). Later nineteenth century Mormons, such as Brigham Young, understood the matter in the same way, and also distinguished between the excessive and judicious use of spirits.
Abraham H. Cannon made an entry in his diary stating that Amasa Lyman saw Joseph Smith smoking the cigar immediately after delivering a sermon on the Word of Wisdom and that he immediately afterward "rode through the streets smoking a cigar" in order to try "the faith of the Saints."[4] At the time that Lyman made this accusation, he had already been excommunicated from the Church.
These sorts of things really call into question a lot of these kinds of stories - especially when they are published long after the events they claim to be portraying (and the cigar story is certainly that). By the time these stories develop, we have these cultural myths being created about Joseph Smith. And so when we have this story about the Amasa Lyman encounter that first shows up in Abraham Canon's journal in 1895, we ought to start with a degree of suspicion. The problem we have with stories like this is that Joseph really did on occasion do things to test the Saints. He liked to go down to the boats at Nauvoo dressed poorly so as to interact with the new converts coming in to Nauvoo and to see what their expectations were. He regularly acted in ways that some thought were inappropriate for a prophet. One of the more widely known stories in the later 19th century was this one, recorded by William Allred and published in 1892:
I was with him [Joseph Smith] in the troubles at DeWitt, Adam-ondi-ahman, and in Far West. I have played ball with him many times in Nauvoo. He was preaching once, and he said it tried some of the pious folks to see him play ball with the boys. He then related a story of a certain prophet who was sitting under the shade of a tree amusing himself in some way, when a hunter came along with his bow and arrow, and reproved him. The prophet asked him if he kept his bow strung up all the time. The hunter answered that he did not. The prophet asked why, and he said it would lose its elasticity if he did. The prophet said it was just so with his mind, he did not want it strung up all the time. Another time when I heard him preaching he said if he should tell the people all the Lord had revealed to him, some would seek his life. Even as good a man as old Father C—-, here on the stand, he added, (pointing back to him) would seek his life.[5]
There is this story, and it sounds like something we might expect, but it tends to have problems when we realize that this entire story is based on a much older story about the New Testament apostle John. Here is a version of that story, published by Fracis De Sales, in 1609:
It is necessary sometimes to relax our minds as well as our bodies by some kind of recreation. St. John the Evangelist, as Cassian relates, was one day found by a huntsman with a partridge on his hand, which he was caressing for his recreation. The huntsman asked how such a man as he could spend his time in so poor and mean an occupation? St. John replied: Why dost thou not carry thy bow always bent? For fear, answered the huntsman, that if it were always bent, it would loose its spring and become useless. Be not surprised, then, replied the apostle, that I should sometimes remit a little of the close application and attention of my spirit and enjoy a little recreation, that I may afterward employ myself more fervently in divine contemplation.[6]
Joseph Smith is reported as drinking tea on a few occasions. Does this make Joseph Smith a hypocrite for violating the Word of Wisdom?
We are sometimes guilty of "presentism"—judging historical figures by the standards of our day, instead of their day.
The Word of Wisdom was enforced differently in the 19th century than today. It was not enforced as rigorously, or with the same requirements, in Joseph Smith's day. It was not the strict test of fellowships that it is for the modern member. Many speakers emphasized the Lord's patience in this matter, as applied to both leaders and members.
But, many of the events described are actually concerned about medical practice, not the social or recreational use of these substances. For example, one might be shocked to learn that President Kimball used morphine—however, the morphine was prescribed for cancer pain by a physician.
Joseph's use of tea may have been an exceptional event, worthy of note in his journal. Why would this be?
In consulting the journal entry, we read: "Saturday, March 11th Too cold last night as to freeze [p.332] water in the warmest rooms in the city. River filled with anchor ice. 8 1/2 o'clock in the office, Joseph said he had tea with his breakfast." [7]
In Joseph's day, some medical thinking held that "hot drinks" (such as tea and coffee) could heat the body and vital fluids. While this was usually regarded as a bad idea that would be dangerous to health:
I found, after maturely considering the subject, that all animal bodies are formed of the four elements, earth, air, fire, and water. Earth and water constitute the solids, and air and fire, or heat, are the cause of life and motion. That cold, or lessening the power of heat, is the cause of all disease; that to restore heat to its natural state, was the only way by which health could be produced;....a state of perfect health arises from a due balance or temperature of the four elements; but if it is by any means destroyed, the body is more or less disordered. And when this is the case, there is always an actual diminution or absence of the element of fire, or heat; and in proportion to this diminution or absence, the body is affected by its opposite, which is cold. And I found that all disorders which the human family were afflicted with, however various the symptoms, and different the names by which they are called, arise directly from obstructed perspiration, which is always caused by cold, or want of heat ....[8]
This entry is from the works of Samuel Thomson, a founder of what became known as "Thomsonian herbalism." There were several Latter-day Saint physicians who were Thomsonians, including (significantly) Willard Richards, who wrote the diary entry we are here considering. The emphasis on loss of heat and lack of stimulation is significant—for it clashed with another set of medical principles, the "orthodox" or "heroic" doctors who came to believe that acute disease was not caused by lack of heat, but by too much energy, heat, or vital force: hence their prescriptions for bleeding, purging, and the like: to lower the energy or "heat." [9] Thus, under normal circumstances an 'energizing', 'hot', or 'stimulating' drink would be inappropriate.
There might, however, be exceptions. Thomson described a local woman who acted as a healer, and his admiration for her skill and methods is clear:
There was an old lady by the name of Benton lived near us, who used to attend our family when there was any sickness. At that time there was no such thing as a Doctor known among us, there not being any within ten miles. The whole of her practice was with roots and herbs, applied to the patient, or given in hot drinks, to produce sweating; which always answered the purpose. [10]
Thus, in a time of extreme cold, a "hot drink" like tea could be seen as a medicinal or preventative treatment which would help maintain health, since it would prevent the loss of the vital heat upon which the body depended. As a Thomsonian physician, Willard Richards (who wrote Joseph's journal for him) would have known and preached this. An "orthodox physician" (wary of heat, and more apt to bleed or purge) would have vigorously disagreed. [11]
By analogy, a modern member would be in violation of the Word of Wisdom if he or she injected morphine as a "recreational" drug. But, if the same drug was administered for a medical reason, the member would not be at fault. (Indeed, we might find fault with someone for refusing a medical treatment to maintain their health or cure an illness.)
That Richards was not surprised or offended by Joseph's consumption of tea on a bitterly cold winter morning demonstrates that Joseph's action was not the scandal that some wish to portray it as.
As one historian observed in 1972:
While the Saints opposed the common use of tea and coffee, it would appear that they had little objection to its occasional use for medicinal purposes. In an age when these items were frequenlty used as a relief for a wide variety of ailments, it would have been imprudent to have entirely forbidden their use.[12]
Some critics of the Church hope their readers will be shocked by George A. Smith's admission that Emma Smith offered some new converts a glass of tea. But, why would George A. Smith admit to Joseph committing a grave sin, if such it was? His account provides us with the clues:
I know persons who apostatized because they supposed they had reasons; for instance, a certain family, after having travelled a long journey, arrived in Kirtland, and the prophet asked them to stop with him until they could find a place. Sister Emma, in the mean time, asked the old lady if she would have a cup of tea to refresh her after the fatigues of the journey, or a cup of coffee. This whole family apostatized because they were invited to take a cup of tea or coffee, after the Word of Wisdom was given. [13]
It is significant that George A. Smith says Emma made the offer "to refresh her after the fatigues of the journey." This is not merely a polite offer of something to drink—it is suggesting that the old woman may be particularly vulnerable to having her "vital heat" diminished by the rigors of a long journey exposed to the elements. Emma is probably making a health-related offer, not just offering a social beverage as we would today. Difficulties in assuring clean water supplies also make tea or coffee a sometimes wiser choice for health. Both coffee and tea are made from boiled water, which will kill bacteria. Even without boiling, the tannic acid in tea would kill the bacteria that caused such scourges as cholera, typhoid, and dysentery—all real risks on the American frontier. [14]
George A. Smith clearly intends his audience to see the converts' action as ridiculous—the Word of Wisdom did not forbid the maintenance of health.
Joseph Smith obtained some tobacco for a friend while in Carthage Jail prior to being martyred. Doesn't this make Joseph Smith a hypocrite for violating the Word of Wisdom?
We are sometimes guilty of "presentism"—judging historical figures by the standards of our day, instead of their day. The tobacco was intended for medicinal purposes.
Willard Richards was a Thomsonian herbalist, a type of physician common in the first half of the nineteenth century in the United States. Thomson was the name of the founder of this school of practice, which differed from the practice of the "orthodox" medical doctors, who focused on balancing humors, purging, inducing diarrhea, and so forth.
An aspect of Thomsonian medicine was Thomson's enthusiasm for the use of lobelia, or wild Indian tobacco. It was used as a cure-all, and was prominently used as an emetic to induce vomiting and restore health. This is the key to understanding the use of tobacco at Carthage Jail.
Neither the wine nor the tobacco was, for members at the time, seen as a violation of the Word of Wisdom--they were likely medicinal.
Willard Richards, who was in jail with Joseph, was a Thomsonian physician. This was a branch of pre-modern medical practice which required minimal schooling. Thomson's followers' believed strongly in the use of lobelia, or wild Indian tobacco. It was used as a cure-all, and was prominently used as an emetic to induce vomiting and restore health. This is the key to understanding the use of tobacco at Carthage Jail.
Critics Gerald and Sandra Tanner (p. 33) make a great deal of Joseph asking for a "pipe and tobacco" for Willard Richards. However, when we understand the circumstances, this action makes sense, and it has nothing to do with the Word of Wisdom. In the first place, we must realize that Joseph and Willard were locked in Carthage Jail.
Joseph had sent Stephen Markham out, as previous text unquoted by the Tanners tells us: "'Brother Markham...go get the doctor [i.e., Richards] something to settle his stomach,' [said Joseph,] and Markham went out for medicine. When he got the remedies desired...[the] Carthage Greys gathered round him, put him on his horse, and forced him out of the town at the point of the bayonet." So, Markham could not return, and none of the remedies he had obtained reached the jail. [15]
It is not clear which remedies Markham sought out—but he could not return. A Thomsonian like Richards would have probably seen tobacco as a medicinal drug, however—especially in a pinch when he could get nothing else. This would be particularly true if the tobacco was lobelia—it was the Thomsonian cure-all, literally.
The Tanners complain elsewhere about how in the History of the Church the words "pipe and some tobacco" were replaced by the word "medicine" (p. 471). But, this misses the point in a spectacular way—tobacco was considered a medicine at the time! Modern editors would not make this type of change to a historical text, but one can understand why rather than bother to explain about Thomsonian beliefs and medical practices, the editors of earlier times decided to simply "translate" the reason for the tobacco. The issue only becomes important, after all, when one is unfamiliar with early nineteenth century medicine.
There is further evidence that the tobacco was not seen as a problem by current or later leaders, since John Taylor's later account of the martyrdom in History of the Church mentions it very frankly and matter-of-factly:
Before the jailer came in, his boy brought in some water, and said the guard wanted some wine. Joseph gave Dr. Richards two dollars to give the guard; but the guard said one was enough, and would take no more.
The guard immediately sent for a bottle of wine, pipes, and two small papers of tobacco; and one of the guards brought them into the jail soon after the jailer went out. Dr. Richards uncorked the bottle, and presented a glass to Joseph, who tasted, as also Brother Taylor and the doctor, and the bottle was then given to the guard, who turned to go out. When at the top of the stairs some one below called him two or three times, and he went down.[16]
Since neither the wine nor the tobacco was, for members at the time, seen as a violation of the Word of Wisdom. Leaders would not include this information if it made Joseph look bad. This should be our first clue that something else is going on.[17] Some critics, however, have not sought to understand, but merely to condemn by trusting that their audience will not understand the fine points of early nineteenth century frontier medicine.
Critical sources |
|
Joseph's prophecy of drinking wine with Hyde in Palestine is reminiscent of Jesus' promise to the apostles that he would drink of wine when the kingdom of God was come (Luke 22:18) which was reiterated in a revelation to Joseph Smith (D&C 27꞉5). Joseph prophesied that he would drink with Hyde there—but whether he would go to Palestine in this life was something about which he immediately expressed uncertainty.
Those who offer this criticism make three errors:
Joseph was not certain that he would see Palestine during this life. As can be seen below, Joseph (1) prophesied that he would drink wine with Hyde in the Holy Land; and then (2) expressed hope that he would go with the Twelve to the Holy Land, but was aware he might not live, and left the matter to God's will:
Elder Hyde told of the excellent white wine he drank in the east [Palestine]. Joseph prophesied in the name of the Lord that he would drink wine with him in that country. Joseph [said], "From the 6th day of April next, I go in for preparing with all present for a Mission through the United States and when we arrive {page 143} at Maine we will take ship for England and so on to all countries where we are a mind for to go." P[r]e[se]nt: H[yrum] Smith, B[righam] Young, H[eber] C. Kimball, Orson Hyde, Orson Pratt, John Taylor, W[ilford] Woodruff, Geo[rge] A. Smith, [and] W[illard] Richards.
[Joseph said,] "We must write for John E. Page. We must love the whole Quorum. We must send Kings and Queens to Nauvoo and we will do it. We must all start from this place. Let the 12 [Apostles] be called in on the {page 143} 6th of April and a notice be given for a special conference on the platform on [the] House of the Lord. We are sure to go as we live till spring. If I live I [will] take these b[r]ethren through these United States and through the world. I will make just as big a wake as God Almighty will let me."[18]
Once again, critics count on their audience thinking that the prophets have commanded the same degree of observance of the Word of Wisdom throughout Church history.
Critical sources |
|
Video |
|
Navigators |
Life and Character |
|
Youth |
|
Revelations and the Church |
|
Prophetic Statements |
|
Society |
|
Plural marriage (polygamy) |
|
Death |
Is it possible that Joseph Smith is not a martyr because, while in jail, he had a gun and he had the temerity to defend himself, his brother, and his friends?
It seems clear that:

In order to make their argument tenable, the critics must do three things. First, they must take some creative liberties with the English language. In this case, the word being redefined is the term martyr. Webster’s New World Dictionary defines a "martyr" as
The online resource, Dictionary.com, defines a martyr as
"one who chooses to suffer death rather than renounce religious principles."[20]
Both are nearly identical and fairly standard definitions, and neither includes a requirement or qualifiers of any sort. However, some anti-Mormon writers have taken the term martyr and subtly changed its definition to suit their own needs. The new definition would probably read something like this: Martyr: a person who chooses to suffer or die rather than give up his faith or his principles without any resistance or effort at self-defense on his part whatsoever.
Critics are free to use such a definition, but it belongs to them alone; it is not the standard use of the word, and not what Church members mean when they refer to the "martyrdom" of Joseph and Hyrum Smith at Carthage.
Throughout Christian history, "martyrs" have been understood to be those who suffered quietly, and those who resisted, even with violence, and even to the death of those who persecuted them for their beliefs.
The first anti-Mormon argument thus focuses on the fact that Joseph had a firearm and that he used that firearm to defend himself. Is it possible that Joseph's announcement that he was going "as a lamb to the slaughter" is false, since he fought back?
Anyone who has ever worked on a farm or in a slaughterhouse knows that sheep do not go willingly to the slaughter. They kick and buck, bleat, scream, and make every attempt to escape their fate. In fact, they make such a haunting sound, that the title of an extremely popular Hollywood film was based on it: The Silence of the Lambs. The term "lamb to the slaughter" simply refers to the inevitability of the final outcome. No matter how valiantly they struggle, the fate of the sheep is sealed. If we apply this understanding to Joseph Smith and his brother, it is clear that they truly were slaughtered like lambs. Fight as they might, they were doomed.
| Related articles: | Martyrdom in Christian history Summary: Christians have never required someone to go passively and unresisting to their death to be considered a martyr. |
| Joseph Smith's qualification as a martyr Summary: By any reasonable definition, Joseph and Hyrum were martyrs for their faith. |
Some claim that the Church has tried to hide the fact that Joseph fired a pepperbox pistol at the mob which murdered Hyrum and was soon to kill him.

Joseph's gun is on display at the Church History Museum in Salt Lake City, where anyone can see it. It has been there for years.
There is overwhelming evidence that from the earliest days following the martyrdom, to the present, that both official and unofficial Church publications have repeatedly mentioned Joseph's pistol.

From the very beginning of the Church, Joseph's possession and use of a pepperbox pistol in defense of himself and his brother and friends has been repeatedly mentioned. This includes statements by LDS, anti-Mormon, and other secular sources even from a very early period, demonstrating that there was no attempt to hide the facts.
martyrdom and actually shows the smoking gun in Joseph's hand (circa this date). This was a traveling show of huge painted canvases that would be displayed to LDS audiences.
There was to be one great final lesson before his mortal life ended. He was incarcerated in Carthage Jail with his brother Hyrum, with John Taylor, and with Willard Richards. The angry mob stormed the jail; they came up the stairway, blasphemous in their cursing, heavily armed, and began to fire at will. Hyrum was hit and died. John Taylor took several balls of fire within his bosom. The Prophet Joseph, with his pistol in hand, was attempting to defend his life and that of his brethren, and yet he could tell from the pounding on the door that this mob would storm that door and would kill John Taylor and Willard Richards in an attempt to kill him. And so his last great act here upon the earth was to leave the door and lead Willard Richards to safety, throw the gun on the floor, and go to the window, that they might see him, that the attention of this ruthless mob might be focused upon him rather than the others. Joseph Smith gave his life. Willard Richards was spared, and John Taylor recovered from his wounds. "Greater love hath no man than this, that a man lay down his life for his friends." The Prophet Joseph Smith taught us love—by example.
In the Church History Museum near Temple Square, located inside a glass case, resides a pair of 19th century pistols and a walking stick. The placard reads, in part, as follows,
Joseph’s Pepperbox Pistol and Hyrum’s Single Shot Pistol. These guns were used by both men for their defense during the attack at Carthage
These were the guns that were smuggled into the Carthage Jail while Joseph Smith, Hyrum and their friends awaited their fate. On the morning of June 27, 1844, Cyrus Wheelock visited the jail.
The morning being a little rainy, favoured his wearing an overcoat, in the side pocket of which he was enabled to carry a six-shooter, and he passed the guard unmolested. During his visit in the prison he slipped the revolver into Joseph’s pocket. Joseph examined it, and asked Wheelock if he had not better retain it for his own protection.
This was a providential circumstance, as most other persons had been very rigidly searched. Joseph then handed the single barrel pistol, which had been given him by John S. Fullmer, to his brother Hyrum, and said, "You may have use for this." Brother Hyrum observed, "I hate to use such things, or to see them used." "So do I," said Joseph, "but we may have to, to defend ourselves;" upon this Hyrum took the pistol. [i]Although it was referred to as a "six shooter," the pepper-box pistol was not a revolver in the normal sense. It incorporated six individual barrels, it was difficult to aim and tended to be unreliable. The June 2013 Ensign features a painting Greater Love Hath No Man, by Casey Childs. [ii] The artwork features all three items in the display case. Joseph, Hyrum and Willard Richards are attempting to hold the door shut as the mob attempts to enter the room. John Taylor is holding his walking stick. In Hyrum’s left pocket is the single shot pistol brought into the jail by Fullmer, and in Joseph’s left pocket, clearly visible, is the pepper-box pistol given to him by Wheelock.
Critical sources |
|
Joseph fired his gun six times (only three shots discharged) and he hit two of the mobbers, which John Taylor later mistakenly stated had died. Was Joseph a murderer?
Joseph's actions were clearly self-defense and defense of others under the common law. However, this point is moot since the attackers who were hit were not killed (as was first reported in some Church publications) but only wounded. They were alive and well at the trial held for mob leaders, and were identified by witnesses. Their good health allowed them to receive gifts because of their role in the assault on Joseph, Hyrum, and the other prisoners.
According to Dallin Oaks and Marvin Hill:
Wills, Voras, and Gallaher were probably named in the indictment because their wounds, which testimony showed were received at the jail, were irrefutable evidence that they had participated in the mob. They undoubtedly recognized their vulnerability and fled the county. A contemporary witness reported these three as saying that they were the first men at the jail, that one of them shot through the door killing Hyrum, that Joseph wounded all three with his pistol, and that Gallaher shot Joseph as he ran to the window.[Hay, "The Mormon Prophet's Tragedy," 675] According to Hay, Wills, whom the Mormon prophet had shot in the arm, was an Irishman who had joined the mob from "his congenital love of a brawl."[Statement of Jeremiah Willey, August 13, 1844, Brigham Young correspondence, Church Archives.] Gallaher was a young man from Mississippi who was shot in the face.[Hay, "The Mormon Prophet's Tragedy," 669, 675. Another source says Wills was a former Mormon elder who had left the Church. Davis, An Authentic Account, 24.] Hay described Voras (Voorhees) as a "half-grown hobbledehoy from Bear Creek" whom Joseph shot in the shoulder. The citizens of Green Plains were said to have given Gallaher and Voras new suits of clothes for their parts in the killing.[Statement of Jeremiah Willey, August 13, 1844][21]
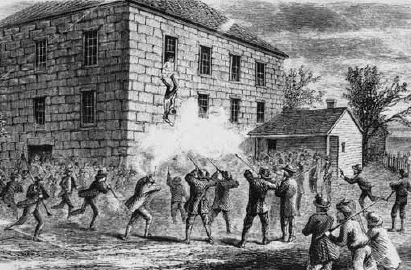
Many members of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (and this is especially true of new members or less-active members) are not aware of all the excruciatingly minute details of the history of the Church. It has become a common tactic among some anti-Mormon aficionados of Mormon history to use this historical ignorance as a weapon. These writers often claim to "expose" these minor events of Church history in a sensationalistic attempt to shock members of the Church with "hidden" revelations or "secret" accounts about various episodes in Church history. They will often claim that the Church has kept this knowledge under wraps for fear that if it was generally known it would cause many members of the Church to immediately renounce their faith and result in the ruination of the Church.
Unfortunately for the critics, Joseph's attempt to defend himself, his brother, and his friends, and his possession of a pepperbox gun, is clearly spelled out in the History of the Church:
In the meantime Joseph, Hyrum, and Elder Taylor had their coats off. Joseph sprang to his coat for his six-shooter, Hyrum for his single barrel, Taylor for Markham's large hickory cane, and Dr. Richards for Taylor's cane. All sprang against the door, the balls whistled up the stairway, and in an instant one came through the door.
Joseph Smith, John Taylor and Dr. Richards sprang to the left of the door, and tried to knock aside the guns of the ruffians...
Joseph reached round the door casing, and discharged his six shooter into the passage, some barrels missing fire. Continual discharges of musketry came into the room. Elder Taylor continued parrying the guns until they had got them about half their length into the room, when he found that resistance was vain, and he attempted to jump out of the window, where a ball fired from within struck him on his left thigh, hitting the bone, and passing through to within half an inch of the other side. He fell on the window sill, when a ball fired from the outside struck his watch in his vest pocket, and threw him back into the room.[22]
The next volume of the History of the Church tells the story from John Taylor's point of view:
I shall never forget the deep feeling of sympathy and regard manifested in the countenance of Brother Joseph as he drew nigh to Hyrum, and, leaning over him, exclaimed, 'Oh! my poor, dear brother Hyrum!' He, however, instantly arose, and with a firm, quick step, and a determined expression of countenance, approached the door, and pulling the six-shooter left by Brother Wheelock from his pocket, opened the door slightly, and snapped the pistol six successive times; only three of the barrels, however, were discharged.[23]
If the Church wished to hide these facts, why did they publish them in the History of the Church not once, but twice?
Critical sources |
|
Martyrdom endows a prophet’s testimony with a special validity. Indeed the Greek root “martureo” from which the English word “martyr” is derived means “witness.” The prophet Abinadi is described as “having sealed the truth of his words by his death.”30 Jesus’ own death was a testament of His divinity and mission. He is declared in Hebrews to be “the mediator of the new testament” validated by His death, “For where a testament is, there must also of necessity be the death of the testator. For a testament is of force after men are dead.” [31]
“Like most of the Lord's anointed in ancient time, [Joseph Smith] sealed his mission and his works with his own blood.” [32] In a hail of bullets on the afternoon of June 27, 1844, in Carthage, Illinois, Joseph and his brother, Hyrum, were cut down for the religion and testimony they professed. As the latter-day apostles then announced, “The testators are now dead, and their testament is in force. . . . Their innocent blood on the banner of liberty, and on the magna charta of the United States, is an ambassador for the religion of Jesus Christ, that will touch the hearts of honest men among all nations.” [33]
To see citations to the critical sources for these claims, click here

FAIR is a non-profit organization dedicated to providing well-documented answers to criticisms of the doctrine, practice, and history of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.
We are a volunteer organization. We invite you to give back.
Donate Now