
FAIR is a non-profit organization dedicated to providing well-documented answers to criticisms of the doctrine, practice, and history of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.
Jump to Subtopic:
Jump to details:
Jump to details:
Jump to details:
| Main articles: | Hemispheric geography theory (HGT) |
| Limited geography theory (LGT) | |
| Transporting the plates to New York in a LGT model? |
Life and Character |
|
Youth |
|
Revelations and the Church |
|
Prophetic Statements |
|
Society |
|
Plural marriage (polygamy) |
|
Death |

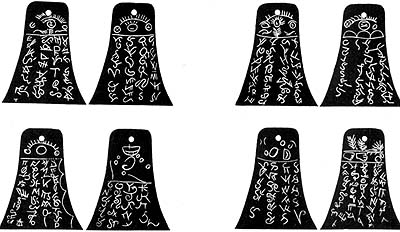
A set of small plates, engraved with characters of ancient appearance, were purported to have been unearthed in Kinderhook, Illinois, in April 1843. The so-called "Kinderhook plates" have been something of an enigma within the Mormon community since they first appeared. While there are faithful LDS who take a number of different positions on the topic of these artifacts, most have concluded that they were fakes.
Joseph Smith appears to have had the plates in his possession for about five days.
Joseph Smith's personal secretary, William Clayton said,
President Joseph has translated a portion [of the Kinderhook plates], and says they contain the history of the person with whom they were found; and he was a descendant of Ham, through the loins of Pharaoh, King of Egypt, and that he received his kingdom through the ruler of heaven and earth.
Chemical analysis performed by the Chicago Historical Society on one of the plates in 1981 showed that the plates were fake.[1] Before the release of the CHS' analysis, criticism of the episode from those outside of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints was infrequent.[2] After the release, criticism became much more frequent.[3] All critics have believed that this episode brings into question any claim of "inspiration" that Joseph used to translate the Kinderhook Plates and by extension any other revelations he received.
However, Joseph Smith "translated" a portion of those plates, not by claiming inspiration, but by comparing characters on the plates to those on his "Grammar and Alphabet of the Egyptian Language" (GAEL). (The GAEL was composed in Kirtland about the time of the translation of the Book of Abraham.) Joseph found one of the most prominent characters on the plates to match a character on the second page of characters in the GAEL. Both were boat shaped. The GAEL interpretation of this boat-shaped character included everything that William Clayton said Joseph said.
Corroborating this is a letter in the New York Herald for May 30th, 1843, from someone who signed pseudonymously as "A Gentile." Research shows "A Gentile" to be a friendly non-Mormon then living in Nauvoo by the name of Sylvester Emmons.[4] He wrote:
The plates are evidently brass, and are covered on both sides with hieroglyphics. They were brought up and shown to Joseph Smith. He compared them, in my presence, with his Egyptian Alphabet…and they are evidently the same characters. He therefore will be able to decipher them.
We know that Joseph was interested in languages. He studied Greek, Hebrew, and German in a secular manner. Therefore, we can easily believe that he attempted to translate the Kinderhook plates without assuming prophetic powers, which powers consequently remain credible.
There exist several accounts that describe the plates. Not all of the account agree on the details.
I have seen 6 brass plates which were found in Adams County by some persons who were digging in a mound. They found a skeleton about 6 feet from the surface of the earth which was 9 foot high. [At this point there is a tracing of a plate in the journal.] The plates were on the breast of the skeleton. This diagram shows the size of the plates being drawn on the edge of one of them. They are covered with ancient characters of language containing from 30 to 40 on each side of the plates. Prest J. has translated a portion and says they contain the history of the person with whom they were found and he was a descendant of Ham through the loins of Pharoah king of Egypt, and that he received his kingdom from the ruler of heaven and earth. [5]
Charlotte Haven claimed to have heard from a friend that Joseph:
said that the figures or writing on them was similar to that in which the Book of Mormon was written...thought that by the help of revelation he would be able to translate them. So a sequel to that holy book may soon be expected.[6]
Brigham Young also drew an outline of one of the Kinderhook plates in a small notebook/diary that he kept. Inside the drawing he wrote:
May 3—1843. I had this at Joseph Smith’s house. Found near Quincy.[7]
The Quincy Whig (a newspaper from a local town near Kinderhook) published their reaction to the plates. It reads:
Finally, a company of ten or twelve repaired to the mound, and assisted in digging out the shaft commenced by Wiley. After penetrating the mound about 11 feet, they came to a bed of limestone, that had apparently been subjected to the action of fire, they removed the stone, which were small and easy to handle, to the depth of two feet more, when they found SIX BRASS PLATES, secured and fastened together by two iron wires, but which were so decayed, that they readily crumbled to dust upon being handled. The plates were so completely covered with rust as almost to obliterate the characters inscribed upon them; but after undergoing a chemical process, the inscriptions were brought out plain and distinct... [8]
Mr. Smith has had those plates, what his opinion concerning them is, we have not yet ascertained. The gentleman that owns them has taken them away, or we should have given a fac simile of the plates and characters in this number. We are informed however, that he purposes returning with them for translation; if so, we may be able yet to furnish our readers with it.
Joseph Smith's journal entry for 7 May 1843 reads:
May 7[th] Sunday 1843. forenoon visited by several gentlemen concerning the plates which were dug out of a mound near quncy [Quincy] sent by Wm Smith to the office for Hebrew Bible & Lexicon— Mr Vickers the wire dancer called. A.M.— court of 1st Preside[n]cy met & adjond [adjourned] one week, 2 P.P. [p.m.] 399President not well— councellors acted.—
evening preaching by Elder [Orson] Hyde text Luke 21 chapter.[9]
Parley P. Pratt's account conflicts with Clayton's in some regards:
Six plates having the appearance of Brass have lately been dug out of a mound by a gentleman in Pike Co. Illinois. They are small and filled with engravings in Egyptian language and contain the genealogy of one of the ancient Jaredites back to Ham the son of Noah. His bones were found in the same vase (made of Cement). Part of the bones were 15 ft. underground. ... A large number of Citizens have seen them and compared the characters with those on the Egyptian papyrus which is now in this city. [10]
Comparison of Clayton and Pratt Accounts of Kinderhook Plates
| Story Element | Clayton Account | Clayton Correct? | Pratt Account | Pratt Correct? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Skeleton | Yes | Incorrect | Yes | Incorrect |
| Size skeleton | 9 feet | Incorrect | Normal size | Incorrect |
| Depth buried | 6 feet | Incorrect | 15 feet | Incorrect |
| Location plates | On breast of skeleton | Incorrect | No mention | N/A |
| Dig site | Adams county | Incorrect | Pike county | Correct |
| Cement vase | No mention | Correct | Mention | Incorrect |
The contents of the Plates, together with a Fac-simile of the same, will be published in the ‘Times & Seasons,’ as soon as the translation is completed.[11]
Wilbur Fugate, one of the perpetrator's of the hoax, wrote a few decades later:
Our plans worked admirably. A certain Sunday was appointed for the digging. The night before, Wiley went to the Mound where he had previously dug to the depth of about eight feet, there being a flat rock that sounded hollow beneath, and put them under it. On the following morning quite a number of citizens were there to assist in the search, there being two Mormon elders present (Marsh and Sharp). The rock was soon removed but some time elapsed before the plates were discovered. I finally picked them up and exclaimed, 'A piece of pot metal!' Fayette Grubb snatched them from me and struck them against the rock and they fell to pieces. Dr. Harris examined them and said they had hieroglyphics on them. He took acid and removed the rust and they were soon out on exhibition. Under this rock (which) was dome-like in appearance (and) about three feet in diameter, there were a few bones in the last stage of decomposition, also a few pieces of pottery and charcoal. There was no skeleton found. [12]
Later he declared in affidavit:
Those plates are a HUMBUG, gotten up by Robert Wiley, Bridge Whitton and myself. … None of the nine persons who signed the certificate knew the secret, except Wiley and I. We read in Pratt’s prophecy that ‘Truth is yet to spring out of the earth.’ [The quote is from Parley P. Pratt’s 1837 missionary tract Voice of Warning.] We concluded to prove the prophecy by way of a joke. We soon made our plans and executed them. Bridge Whitton cut them out of some pieces of copper; Wiley and I made the hieroglyphics by making impressions on beeswax and filling them with acid and putting it on the plates. When they were finished we put them together with rust made of nitric acid, old iron and lead, and bound them with a piece of hoop iron, covering them completely with the rust.[13]
Stanley Kimball published findings demonstrating the plates a hoax:
A recent electronic and chemical analysis of a metal plate (one of six original plates) brought in 1843 to the Prophet Joseph Smith in Nauvoo, Illinois, appears to solve a previously unanswered question in Church history, helping to further evidence that the plate is what its producers later said it was—a nineteenth-century attempt to lure Joseph Smith into making a translation of ancient-looking characters that had been etched into the plates.[14]

The following is from Stanley B. Kimball, "Kinderhook Plates Brought to Joseph Smith Appear to Be a Nineteenth-Century Hoax," Ensign, August 1981 off-site
These two oblique references to a “translation” were followed thirteen years later by a more direct published statement that until recently was wrongly thought to have been written by Joseph Smith himself. On September 3 and 10, 1856, the following paragraphs appeared in the Deseret News as part of the serialized “History of Joseph Smith”:
“[May 1, 1843:] I insert fac similes of the six brass plates found near Kinderhook, in Pike county, Illinois, on April 23, by Mr. R. Wiley and others, while excavating a large mound. They found a skeleton about six feet from the surface of the earth, which must have stood nine feet high. The plates were found on the breast of the skeleton, and were covered on both sides with ancient characters.
“I have translated a portion of them, and find they contain the history of the person with whom they were found. He was a descendant of Ham, through the loins of Pharaoh, king of Egypt, and that he received his kingdom from the ruler of heaven and earth.” (Then followed a reprint of material from the Times and Seasons article.)
Although this account appears to be the writing of Joseph Smith, it is actually an excerpt from a journal of William Clayton. It has been well known that the serialized “History of Joseph Smith” consists largely of items from other persons’ personal journals and other sources, collected during Joseph Smith’s lifetime and continued after the Saints were in Utah, then edited and pieced together to form a history of the Prophet’s life “in his own words.” It was not uncommon in the nineteenth century for biographers to put the narrative in the first person when compiling a biographical work, even though the subject of the biography did not actually say or write all the words attributed to him; thus the narrative would represent a faithful report of what others felt would be helpful to print. The Clayton journal excerpt was one item used in this way. For example, the words “I have translated a portion” originally read “President J. has translated a portion. …”

Don Bradley presented compelling evidence during his 2011 FAIR Conference presentation that Joseph Smith did indeed attempt to translate a character on the Kinderhook Plates.[15] Bradley noted that William Clayton's account is likely representing personal and specific knowledge acquired from Joseph Smith, since evidence indicates that he made his journal entries that day while he was at the Prophet's home. Clayton's account states that
Prest J. has translated a portion and says they contain the history of the person with whom they were found and he was a descendant of Ham through the loins of Pharoah king of Egypt, and that he received his kingdom from the ruler of heaven and earth.
Bradley noted that one of the most prominent characters on the Kinderhook Plates (a symbol shaped like a boat), when broken down into its individual elements matched a symbol found on page 4 (the second page of characters) of the Grammar and Alphabet of the Egyptian Language (GAEL), often referred to as the "Egyptian Alphabet. The GAEL provides meanings for the individual symbols, and the meaning assigned to the particular symbol found on the plates supports the translation reported to have been provided by Joseph.
The conclusion is that Clayton's account appears to be accurate, that Joseph did attempt to translate "a portion" of them by non-revelatory means, and the translation provided matches a corresponding symbol and explanation in the GAEL.

At the time that Joseph Smith translated the Book of Mormon, he only claimed the ability to translate by the "gift and power of God." Over time, Joseph studied other languages and wished to learn to translate by other means. His attempt to use the Grammar and Alphabet of the Egyptian Language (a document that he and others had created) to attempt a translation of the Kinderhook Plates fits in with this desire. Since only a single character "matched," Joseph would have been unable to continue to translate the plates in this manner. This may explain why such a translation was never produced: beyond the single character which happened to match, it would not have even been possible to translate the fraudulent plates either manually or by the "gift and power of God." Therefore, no translation was ever produced.
A critical graphic from "mormoninfographics" states that "Joseph didn't discern the fraud. The LDS Church now concedes it's a hoax. What does this tell us about Joseph Smith's gift of translation?"
Simply put, Joseph's attempt to translate the plates manually tells us that he didn't attempt to translate the plates using the "gift and power of God."
It should be noted that the critical "mormoninfographic" includes a portion of a quote from History of the Church that is written as if it came from Joseph Smith.
The graphic is correct, but it is useful to know the actual source of the quote used by History of the Church.:
I insert fac-similes of the six brass plates found near Kinderhook, in Pike county, Illinois, on April 23, by Mr. Robert Wiley and others, while excavating a large mound. They found a skeleton about six feet from the surface of the earth, which must have stood nine feet high. The plates were found on the breast of the skeleton and were covered on both sides with ancient characters. I have translated a portion of them, and find they contain the history of the person with whom they were found. He was a descendant of Ham, through the loins of Pharaoh, king of Egypt, and that he received his kingdom from the Ruler of heaven and earth.
The quote in question was written in William Clayton's journal. It was rewritten in the first person (as if Joseph Smith had said it himself) when it was included in History of the Church. Clayton's journal is the primary source, which was used in History of the Church (a secondary source).
The quote by William Clayton is indeed accurate: Joseph Smith did attempt to translate a portion of the Kinderhook Plates. This is explained in the following section.
The following is from Stanley B. Kimball, "Kinderhook Plates Brought to Joseph Smith Appear to Be a Nineteenth-Century Hoax," Ensign, August 1981 off-site
These two oblique references to a “translation” were followed thirteen years later by a more direct published statement that until recently was wrongly thought to have been written by Joseph Smith himself. On September 3 and 10, 1856, the following paragraphs appeared in the Deseret News as part of the serialized “History of Joseph Smith”:
“[May 1, 1843:] I insert fac similes of the six brass plates found near Kinderhook, in Pike county, Illinois, on April 23, by Mr. R. Wiley and others, while excavating a large mound. They found a skeleton about six feet from the surface of the earth, which must have stood nine feet high. The plates were found on the breast of the skeleton, and were covered on both sides with ancient characters.
“I have translated a portion of them, and find they contain the history of the person with whom they were found. He was a descendant of Ham, through the loins of Pharaoh, king of Egypt, and that he received his kingdom from the ruler of heaven and earth.” (Then followed a reprint of material from the Times and Seasons article.)
Although this account appears to be the writing of Joseph Smith, it is actually an excerpt from a journal of William Clayton. It has been well known that the serialized “History of Joseph Smith” consists largely of items from other persons’ personal journals and other sources, collected during Joseph Smith’s lifetime and continued after the Saints were in Utah, then edited and pieced together to form a history of the Prophet’s life “in his own words.” It was not uncommon in the nineteenth century for biographers to put the narrative in the first person when compiling a biographical work, even though the subject of the biography did not actually say or write all the words attributed to him; thus the narrative would represent a faithful report of what others felt would be helpful to print. The Clayton journal excerpt was one item used in this way. For example, the words “I have translated a portion” originally read “President J. has translated a portion. …”
So, a larger conclusion that we can draw is that we’ve got both the smoking-gun – the GAEL that he uses to translate, and we’ve got an eyewitness. We know exactly how Joseph Smith attempted to translate from the Kinderhook plates and obtain the content that Clayton says he did. A larger conclusion, then, that we can draw is that Joseph Smith translated from the Kinderhook plates not by revelation, but by non-revelatory means.
Key sources |
|
Wiki links |
|
FAIR links |
|
Online |
|
Video |
Load video YouTube YouTube might collect personal data. Privacy Policy
Load video YouTube YouTube might collect personal data. Privacy Policy
Load video YouTube YouTube might collect personal data. Privacy Policy |
Print |
|
Navigators |
|
Sub categories |
Critical sources |
|
Jump to details:
Jump to details:
Jump to details:
Latter-day Saints and the Bible |
|
Reliability of the Bible |
|
Creation |
|
Genesis |
|
Understanding the Bible |
|
Cultural issues |
|
The Bible and the Book of Mormon |
|
This page answers scientific and scriptural questions about Noah's Flood.

Church leaders typically treat the Flood as global. The challenge comes when Genesis is read as a scientific account. This reading is then contrasted with modern scientific data showing the diversity of plant and animal life, and the complete lack of evidence for a global Flood in the geological or archaeological record.
The concept of a spherical earth "did not appear in Jewish thought until the fourteenth or fifteenth century." [1]:30 The word "earth," as used in the Bible, simply refers to solid ground or land, as opposed to water (see Genesis 1:10—"God called the dry land Earth; and...the waters called he Seas...."). It is, of course, possible that earlier prophets had a more advanced view of the nature of the earth—this perspective could, however, have been lost to later centuries and scribes.
| Related article: | How did ancient Israel picture the world and the universe? Summary: A spherical earth with stars and planets was not how Israel understood the world. Instead, they saw it as a flat disc, with an underworld beneath, and a rigid dome over top for the heavens. |
Genesis 7꞉19-23 reads:
For those who approach the matter in this way, the primary reason for seeing the Flood as global comes from the word "earth." When modern readers see the word "earth," they envision the entire planetary sphere. Dr. Duane E. Jeffery elaborates:
A critical issue in the Flood story in the King James Bible has to do with translations of the Hebrew words eretz and adamah as meaning the entire "earth." What do these terms actually mean? It is widely recognized that Hebrew is a wonderful language for poets, since virtually every word has multiple meanings. But that same characteristic makes it a horrible language for precision. As it turns out, eretz and adamah can indeed be a geographical reference akin to what we usually mean by "the earth." But it is not at all clear that the ancients had the concept of a spherical planet that you and I do. Many scholars argue that the Bible writers thought in terms of a flat earth that was covered by a bowl-shaped firmament into which the windows of heaven were literally cut[1]:31-32
Jeffrey goes on to note that ideas of a global Flood may have resulted from a widespread local problem. A current hypothesis that has been gaining ground since 1998 is that a significant flooding event occurred in the area now occupied by the Black Sea. Evidence has been discovered which has led a number of researchers to believe that the Black Sea area was once occupied by a completely isolated freshwater lake at a much lower level than the ocean. The theory is that the sea level rose and eventually broke through the Bosporus shelf, resulting in a rapid flooding event which would have wiped out all life living along the shores of the lake (see p. 34). Whether this is the source for the Genesis Flood remains conjecture.
Thus, with this reading the prophets said and meant "the enitre world" but they had a quite different view of what the whole world entailed than we would.
The difficulty with the above, however, is that it reads ancient scripture to address questions that the scripture was probably never meant to address.
Those who study biblical and other texts often talk about the genre of a piece of writing. Genre describes the type of writing that is being studied.
One genre is history; another genre is fiction; another genre is poetry. Readers usually know what genre they are reading, and they adjust their expectations and their way of reading accordingly.
For example, if someone thought that the Lord of the Rings was in the history genre, they might consider it a terribly deceptive work. It describes events and powers for which we have no other evidence. If, however, the reader understands that its genre is fantasy fiction, then the reader expects different things.
Walter Moberly said:
You cannot put good questions and expect fruitful answers from a text apart from a grasp of the kind of material it is in the first place; misjudge the genre, and you may skew many of the things you try to do with the text.[2]
(The 1999 movie Galaxy Quest plays on this idea of mistaken genre—a group of aliens mistake the genre of a Star Trek-like television show. They refer to the show as "historical documents," and believe that the actors really are spacefarers on a spaceship.[3] This is an error of genre, and much of the movie's humor and plot is driven by the contrasts between the expectations of adventure fiction versus historical reality.)
Modern Church leaders and members have sometimes read the Flood story in the genre of what we might call "scientific history"—that is, they read it as a technical description of physical realities in a scientific context. This assumption is called concordism: "assumption that scripture is speaking in scientific terms, and therefore to be true and inspired, it has to match what science says."[4]
This assumption could be true—but it is an assumption, not an obvious truth as some treat it. (And, we must ask—since science in any form didn't really exist until the 1600s, and our modern science didn't really get going until the 1800s, why did God speak to ancient peoples in a form completely foreign to them? "[T]hese things were not in the mind of the authors of Genesis. That was not the audience, or the genre, or the spiritual needs they were speaking to."[4])
As John Walton, an evangelical bible scholar put it:
When we approach a text, we must be able to set our presuppositions off to the side as much as possible so that we do not impose them onto the text. It is not wrong to have presuppositions, but it is important to have a realistic grasp of what our presuppositions are so that we can assess their impact on our interpretation. Some of the traditions we carry as baggage are blind presuppositions…. We don’t even realize that they are imported into the text, and we must evaluate their relevance and truth rather than assume them to be accurate.[5]

So maybe we have the genre wrong. What if we are like the aliens who think Star Trek is science fact, not science fiction?
If ... you compare Genesis to other ancient Near Eastern creation and Flood stories on the left side, Genesis looks very, very different. It makes a lot more sense and there’s much less conflict. This essentially establishes that comparing Genesis with science is comparing apples and oranges. It’s not a legitimate comparison to begin with, because it’s based on unjustified and anachronistic concordist assumptions.[4]
As it happens, "Flood story" is a genre all of its own. The people who wrote and the people who heard the Old Testament had friends and neighbors with Flood stories.
Every serious student of the Bible knows that there are other Flood stories from the ancient Near East, particularly from ancient Sumer, Babylon, and Assyria.l What is disputed is not the existence and relevance of these ancient Flood accounts but rather their significance and relationship to the biblical story. ...
The general contours of the Flood story as we hear it in the Eridu Genesis, Atrahasis, and the Gilgamesh Epic are very similar. Due to displeasure with humans, the divine realm decides to bring a Flood against them to destroy them. In each case, the divine realm chooses one individual (Ziusudra, Atrahasis, Uta-napishti, Noah) to save by warning them of the coming Flood and instructing them to build an ark. While the shape of the arks in the various stories differs, remarkably the floor space of the arks is nearly identical.1 After building the ark, the Flood hero and others (family and in some cases even more people) as well as animals enter the ark. The Flood waters rise and finally ebb to the point that the ark comes to rest. ...
As we begin, the reader should not jump to the conclusion that the identification of similarities suggests that the biblical author has borrowed information directly from the Mesopotamian accounts. Everyone in the ancient world knows there was a Flood (just like everyone today knows there was a Holocaust). It is in the cultural river. The question is, what was God up to? Why did he send it? On this point, different texts may offer vastly different interpretations.[6]:53, 61-62
Walton continues:
The gods in the [Ancient Near East] were motivated by what can be called the "Great Symbiosis." ... [that is,] the gods created people because they were tired of the work involved to meet their own needs. Gods needed food, housing, clothing, and so on, but they did not want to work for it. Once people were created to serve in this way, it becomes necessary for the gods to provide for people (if there is no rain, crops cannot grow and the gods cannot be fed) and protect them (if they are being harried by invaders who steal their food or burn their crops, the gods cannot be cared for). Throughout the literature of the ancient world, we learn it is the mandate to provide for the gods that stands as the principal feature of their religious practice. Performance equals piety. Offense is failure to meet the needs of the gods. The result is codependence.
Not surprisingly, the Mesopotamian interpretation of the Flood is based on the premise of this Great Symbiosis. The gods have not created people for relationship (as Yahweh [Jehovah] had done). The gods live among the people (in temples) so that the people can meet their needs, but they don't really like people—they need people. Yahweh, in contrast, has no needs and actually desires relationship. ...
The Great Symbiosis is consistently refuted in the Old Testament and has no role in the interpretation of the Flood. In the Mesopotamian Flood account the Great Symbiosis explains the actions of the gods at every turn. For them, the operation of the Great Symbiosis is the basis for order in the world. In the interpretation offered in Genesis, disruption of order is the driving idea, but order from the biblical standpoint has nothing to do with the Great Symbiosis. ... [6]:65-66
Instead of being about meeting the gods' needs, in the bible the Flood occurs because of human violence and wickedness. Human behavior is preventing the covenant relationship that Yahweh/Jehovah wants to have with them.
This demonstrates how culture and genre should influence how we read scriptural texts:
Another way to think about the similarities and differences is to acknowledge that the Israelites are embedded in an ancient Near Eastern culture and that God speaks to them there. God gives them revelation that transcends the culture, but he speaks to them within the culture. This is not a matter of imposing the ancient Near East on the Bible (the Bible is an ANE literary document); rather, it involves the acknowledgment that they are within the ancient Near East. It's our responsibility to understand the Flood story within its original context ...[6]:87-88
This idea should be a comfortable one for Latter-day Saints, since modern revelation insists that God speaks in the language and thought forms of his people. In the introduction to the Doctrine and Covenants (a book of modern revelation) the Lord says:
Behold, I am God and have spoken it; these commandments are of me, and were given unto my servants in their weakness, after the manner of their language, that they might come to understanding. And inasmuch as they erred it might be made known; And inasmuch as they sought wisdom they might be instructed; And inasmuch as they sinned they might be chastened, that they might repent; And inasmuch as they were humble they might be made strong, and blessed from on high, and receive knowledge from time to time ( D&C 1꞉24-28 (emphasis added) ).
In a sense, we might say that God always has to "dumb things down" for us! He speaks in our own language and way so we can understand, just as he spoke to ancient Israelites or ancient Nephites in their culture and language so they would understand.
Our mistake comes when we try to read texts written for them through our culture and language, rather than theirs.
In the Ancient Near East the world was understood to have been organized by God (or the gods) out of chaos. And chaos was represented by great roiling waters:
This particular judgment [the Flood] is so devastating that it has even been described as an act of uncreation. Going back to the very opening of Genesis, we read: "In the beginning God created the heavens and the earth. Now the earth was formless and empty [tohu wabohu], darkness was over the surface of the deep" (1:1-2). Before God brought the earth into functional order, it was "formless and empty." It is likely, if not certain, the author intends for us to think of the earth as undifferentiated water. From this formless and empty watery mass God creates a functional and livable earth. The Flood, then, is a reversion to the watery mass, a tohu wabohu state. The pattern we have identified also explains the abundance of intertextual allusions in Genesis 9꞉1 and Genesis 1–2 as well as Genesis 9꞉18-29. We observe, then, that one way of reading Genesis 1–9 is along the lines of creation—uncreation—re-creation.[6]:103
For an ancient Israelite, then, the Flood story describes the destruction of God's ordered, created world because of human sin. The world can no longer fulfill its purpose as things stand. ("This is my work and my glory, to bring to pass the immortality and eternal life of man," [Moses 1꞉39].) A world everywhere full of sin, violence, and rebellion cannot fulfill God's purposes to exalt his children through a covenant relationship.
The Flood is a demonstration of God reestablishing the purpose and order of the world:
Genesis 1–11 is interested in tracking the issue of nonorder, order, and disorder. In this View, the Flood account focuses more on how God is reestablishing a modicum of order in the world as he uses nonorder (the cosmic waters) to obliterate disorder (evil and violence). Of course, the Flood does not totally obliterate disorder, as God acknowledges in Genesis 8꞉21. But it resets the ordering process, and God indicates that the established order will not again be reset by a Flood ( Genesis 8꞉21 ). This view focuses attention on God's continuing plan to establish order (present and future oriented) beyond the act of judging sin (past oriented), though both are legitimate perspectives. ...
When we interpret events like the Flood, we should treat the event as we do with a character. What the narrator does with the Flood is more important than what the Flood does, and what God does through the Flood is most important of all. If this is so, then we need to articulate persuasively what the narrator and God are doing through the Flood.[6]:94-95
Jesus uses the Flood account to give a similar sort of message. He is probably not particularly worried that his audience understand that the entire globe was submerged by water. That is not what they would have thought about. Instead, Jesus uses the Flood as an example of God's purposes for his children again being fulfilled—through him:
- As it was in the days of Noah, so it will be at the coming of the Son of Man. For in the days before the Flood, people were eating and drinking, marrying and giving in marriage, up to the day Noah entered the ark; and they knew nothing about what would happen until the Flood came and took them all away. That is how it will be at the coming of the Son of Man. ( Matthew 24꞉37-39 )
The New Testament thus adopts the Flood story as an illustration of the truth that our God is a God who judges sin. He does not tolerate disobedience, since he understands our propensity to promote ourselves above himself does not lead to our flourishing but to our detriment. In this it is used as an archetypal narrative for future eschatological judgment.[6]:98
Just as the Flood was God's way of reestablishing his purposes for the earth and his children, so Jesus' return in glory will likewise sweep away the things in the world that prevent the full blessing and exaltation of God's children.
If we agree that the Flood is about reestablishing God's purposes, then it is not surprising to see that the Flood is immediately followed by covenants:
The term covenant (berit) appears for the first time in connection with Noah. A covenant, as the English translation rightly implies, is a formal agreement between two parties. In this covenant, God commits himself to the continuance of the world and its inhabitants. Though the words are directed to Noah and his sons, that commitment is given not only to them but to all the creation and its creatures. They don't have to live in fear that God will periodically bring the creation to an end. ... Because this covenant is the first one explicitly mentioned in Scripture, the rainbow is the first sign of a covenant. Later we will see that circumcision is the sign of the Abrahamic covenant ( Genesis 17꞉9-14 ), the sabbath is the sign of the Mosaic covenant ( Exodus 31꞉12-18 ), and the Lord's Supper is the sign of the new covenant ( Luke 22꞉20 ). These signs are like brands. They serve as a reminder to the covenant partners of the relationship established between them.[6]:104-105
Some Latter-day Saint thinkers have understood the matter as referring to the sudden separation of the continents in a catastrophic event. Others have regarded this as a misunderstanding of the text
The Church has no official position, and it does not play much of a role in LDS thought or discourse.
Genesis 10꞉25 contains a passing reference to man called Peleg, who received his name because "in his days was the earth divided". The Hebrew verb פלג (palag) means "separate" or "divide." And, in Psalms 55꞉9 it refers specifically to a division of languages.
Some Latter-day Saints have interpreted this passage with extreme literalness, believing that the earth's tectonic plates, which were once a single land mass, all separated into the continents we know today during the life of a single mortal, instead of over hundreds of millions of years as scientists have theorized. Two of these were Joseph Fielding Smith and Bruce R. McConkie.
Prominently, prior to becoming president of the Church, Joseph Fielding Smith wrote that
in the beginning all of the land surface was in one place as it was in the days of Peleg, ( Genesis 10:25 ) that the earth was divided. Some Bible commentators have concluded that this division was one concerning the migrations of the inhabitants of the earth between them, but this is not the case. While this is but a very brief statement, yet it speaks of a most important event. The dividing of the earth was not an act of division by the inhabitants of the earth by tribes and peoples, but a breaking asunder of the continents, thus dividing the land surface and creating the Eastern Hemisphere and Western Hemisphere.[7]
John Taylor also expressed similar views, albeit more briefly.[8] It is perhaps important to note that then-Elder Smith wrote that "By looking at a wall map of the world, you will discover how the land surface along the northern and southern coast of the American Hemisphere and Europe and Africa has the appearance of having been together at one time." [9] Elder Smith was writing between 1953 and 1966; modern continental drift theory was only beginning to gain acceptance during this period (even by 1977, a geology textbook would note that "a poll of geologists now would probably show a substantial majority who favor the idea of drift," while also providing a substantial critique of the theory.[10]
Here again, however, we are at risk of mistaking genre. Elder Smith was reading with modern concerns and preoccupations.
What if we again tried to read as someone in the ancient near east might read?
A few scriptures, then, refer to the earth being divided:
What do these extensive genealogies at this point in the story tell us?
In perhaps the most important study of Old Testament genealogies in the light of ANE analogues, Robert R. Wilson concluded that
- genealogies are not normally created for historical purposes. They are not intended to be strictly historical records. Rather in the Bible, as well as in the ancient Near Eastern literature and in the anthropological material, genealogies seem to have been created for domestic, political- jural, and religious purposes, and historical information is preserved in the genealogies only incidentally.
They are designed to give people an understanding of their identity. ... [G]enealogies, while including lists of real people in a real past, are first and foremost making theological statements ... .
After the Flood, humans continue to sin ( Genesis 11꞉21-29 ). People unite to build a city and a tower that offends God ...
God thus initiates a new strategy of carrying out his plans and purposes beginning with this one man and his wife, Sarah; through their descendants he will reach the world in order to restore blessing on his human creatures.
Notice the dramatic change in the narrative at this point. Whereas the primeval narrative covers the whole world over what must be an incredibly long period of time, now the focus in the second part, the patriarchal narratives, focuses on one individual— Abraham, then Jacob, then Joseph—and devotes considerable narrative space to a relatively short period of time. We observe that such a shift signals a more intense interest in the details of the events associated with the patriarchs as founding figures of the people of God.[6]:104-105, 110
The verses in Genesis and 1 Chronicles are describing the descendants of Shem. LDS scholar Hugh Nibley viewed Genesis 10꞉25 (which says that in the days of Peleg "the earth was divided") as meaning "the earth was divided among the children of Noah."[11] There is no serious biblical scholarship that reads these verses as implying a rapid drift of the continents—partly because such an idea would have been utterly foreign to writers in that time period.
If we read outside of genre and try to turn this into a scientific account, we run into enormous absurdities. Some conclude that this means the bible must be false, but instead it means they are making a genre mistake.
In the December 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake, 1,000 miles of fault line slipped 50 feet, resulting in a 9.3-magnitude earthquake that created seismic sea waves up to 100 feet high. These tsunamis caused the deaths of nearly 230,000 people. The amount of force required to move the major continents thousands of miles apart in the lifetime of a single individual would cause much worse devastation, a global catastrophe on an unimaginable scale.
Thus, to accomplish this without a divine miracle which hid all trace of such an event would be extraordinarily unlikely. But, such a miracle cannot be proven or identified by science or observation.
Those who choose to believe that this is what happen can only rely on faith.
If the division is instead one of language, then D&C 133꞉22–23 would refer to the return to a time when languages no longer divide humankind. This will take place during the 1,000 years of peace when the Savior reigns.
Such a return to unity might also symbolize the passing of all the temporary, petty, and earthly matters which alienate humans from each other.
This seems a far more important idea, and a far more likely issue to discuss with bronze age Israelites, than continental drift.
Members and others sometimes ask how Abraham, Moses and other near eastern Bible prophets ended up in the Old World if Adam and Eden were in the Americas. A variety of approaches have been suggested for this issue:[12]
The solution chosen by an individual member will probably depend mostly on their attitudes to other issues about which there is no official Church position and a variety of positions espoused by members. These issues include matters such as the issue of Death before the Fall, Evolution, Pre-Adamites, the nature of Noah's Flood, the extent to which scripture ought to be interpreted literally, and related topics.

FAIR is a non-profit organization dedicated to providing well-documented answers to criticisms of the doctrine, practice, and history of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.
We are a volunteer organization. We invite you to give back.
Donate Now